Nodal Lymphangiography and Embolization for Postoperative Lymphatic Leakage
- PMID: 40384909
- PMCID: PMC12078084
- DOI: 10.22575/interventionalradiology.2024-0012
Nodal Lymphangiography and Embolization for Postoperative Lymphatic Leakage
Abstract
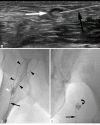
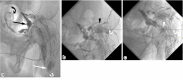
Intranodal lymphangiography has replaced conventional pedal lymphangiography and has advanced lymphatic intervention. In this method, a lymph node is punctured and Lipiodol is injected to visualize the subsequent lymphatic vessels. This has facilitated the widespread adoption of lymphatic interventional radiology due to the simplicity of the technique and the shortened examination time of the procedure, which allows easy mapping of lymphatic vessels and lymphatic fluid dynamics. With this technique, lymphatic embolization was achieved by injecting an embolic substance into the lymph nodes upstream of the lymphatic leak. Although complications associated with lymphangiography are rare, caution should be exercised due to potential complications associated with the use of Lipiodol. This study summarizes intranodal lymphangiography techniques, complications, and lymphatic embolization.
Keywords: intranodal lymphangiography; lipiodol; lymphatic embolization; lymphocele; lymphorrhea.
© 2025 Japanese Society of Interventional Radiology.
Conflict of interest statement
None
Figures
References
-
- Wallace S, Jackson L, Greening RR. Clinical applications of lymphangiography. Am J Roentgenol Radium Ther Nucl Med. 1962; 88:97-109. - PubMed
-
- Cope C. Percutaneous transabdominal embolization of thoracic duct lacerations in animals. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 1996; 7:725-731. - PubMed
-
- Cope C, Salem R, Kaiser LR. Management of chylothorax by percutaneous catheterization and embolization of the thoracic duct: prospective trial. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 1999; 10:1248-1254. - PubMed
-
- Nadolski GJ, Itkin M. Feasibility of ultrasound-guided intranodal lymphangiogram for thoracic duct embolization. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2012; 23:613-616. - PubMed

