Characterization of Gαs and Gαolf activation by catechol and non-catechol dopamine D1 receptor agonists
- PMID: 40384932
- PMCID: PMC12084000
- DOI: 10.1016/j.isci.2025.112345
Characterization of Gαs and Gαolf activation by catechol and non-catechol dopamine D1 receptor agonists
Abstract
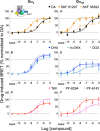
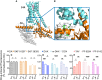
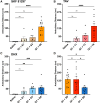
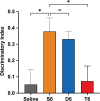
The dopamine D1 receptor (D1R) couples to Gαs and Gαolf and is crucial in regulating neurological and neuropsychiatric functions. In the brain, Gαolf is predominantly found in the striatum whereas Gαs is expressed elsewhere. Our in vitro assays revealed that the tetracyclic catechol agonists dihydrexidine, methyl-dihydrexidine, doxanthrine, and the non-catechol compounds PF-8294, PF-6142 exerted full agonism for Gαs coupling but only partial agonism for Gαolf coupling. In contrast, the non-catechol agonist tavapadon acted as a full agonist at Gαolf and a partial agonist at Gαs. The effects of these ligands on the thalamocortical and striatonigral electrophysiological events, as well as on the locomotor activity and cognitive function of mice agreed with their selectivity profiles in vitro. These findings suggest the possibility of achieving region-specific pharmacology and open new directions for developing D1R drugs to treat relevant neurological and neuropsychiatric disorders.
Keywords: Molecular biology; Neuroscience.
© 2025 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures




References
-
- Waszczak B.L., Martin L.P., Finlay H.E., Zahr N., Stellar J.R. Effects of individual and concurrent stimulation of striatal D1 and D2 dopamine receptors on electrophysiological and behavioral output from rat basal ganglia. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2002;300:850–861. doi: 10.1124/jpet.300.3.850. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Vermeulen R.J., Drukarch B., Sahadat M.C., Goosen C., Wolters E.C., Stoof J.C. The dopamine D1 agonist SKF 81297 and the dopamine D2 agonist LY 171555 act synergistically to stimulate motor behavior of 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine-lesioned parkinsonian rhesus monkeys. Mov. Disord. 1994;9:664–672. doi: 10.1002/mds.870090613. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

