Synovial fluid fibrin degradation product can be used as a new auxiliary marker for periprosthetic joint infection diagnosis
- PMID: 40384983
- PMCID: PMC12082038
- DOI: 10.3389/fcimb.2025.1435970
Synovial fluid fibrin degradation product can be used as a new auxiliary marker for periprosthetic joint infection diagnosis
Abstract
Background: While the value of blood coagulation markers, such as D-Dimer, Fibrinogen, platelet count/mean platelet volume ratio (PC/MPV), and Fibrin Degradation Product (FDP), in the diagnosis of periprosthetic joint infection (PJI) has been explored in recent years, the significance of synovial fluid coagulation markers in PJI diagnosis remains unclear. Therefore, this study aims to investigate the potential value of synovial fluid D-Dimer (sD-Dimer) and synovial fluid FDP (sFDP) in the diagnosis of PJI.
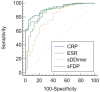
Materials and methods: In a prospective study, the levels of serum C-reactive Protein (CRP), Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate (ESR), sD-Dimer, and sFDP were measured and compared in 56 patients with PJI (Group A) and 40 patients with aseptic loosening (Group B) who presented at our department from March 1st, 2020, to December 31st, 2023. The diagnostic efficacy of these markers in PJI diagnosis was assessed using the area under the curve (AUC) of the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve.
Results: The levels of CRP, ESR, sD-Dimer, and sFDP in Group A were significantly higher than the levels in Group B. The AUC values, optimal threshold values, sensitivity, and specificity for CRP, ESR, sD-Dimer, and sFDP in PJI diagnosis were as follows: CRP [0.920 (95% confidence interval (CI), 0.846-0.965), >6.77, 76.69%, 95.00%], ESR [0.905 (95% CI, 0.828-0.955), >41, 73.21%, 92.50%], sD-Dimer [0.788 (95% CI, 0.692-0.864), >738.65, 66.07%, 80.00%], and sFDP [0.869 (95% CI, 0.785-0.929), >1558.35, 91.07%, 70.00%]. Furthermore, sFDP demonstrated similar performance in PJI diagnosis to CRP and ESR, while sD-Dimer exhibited inferior performance in PJI diagnosis compared to CRP and ESR.
Conclusions: sFDP shows promise as a valuable new adjunctive diagnostic marker for PJI. Further investigations with larger sample sizes are warranted.
Keywords: CRP; D-dimer; ESR; diagnosis; fibrin degradation product; prosthetic joint infection; synovial fluid.
Copyright © 2025 Huang, Chen, Zhang, Cheng, Peng, Li, Meng, Liu and Jin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Exciting Performance of Plasma Fibrinogen in Periprosthetic Joint Infection Diagnosis.Orthop Surg. 2021 May;13(3):812-816. doi: 10.1111/os.12964. Epub 2021 Mar 15. Orthop Surg. 2021. PMID: 33719200 Free PMC article.
-
Synovial Fluid Viscosity Test is Promising for the Diagnosis of Periprosthetic Joint Infection.J Arthroplasty. 2019 Jun;34(6):1197-1200. doi: 10.1016/j.arth.2019.02.009. Epub 2019 Feb 13. J Arthroplasty. 2019. PMID: 30837099 Clinical Trial.
-
Plasma D-dimer Does Not Anticipate the Fate of Reimplantation in Two-stage Exchange Arthroplasty for Periprosthetic Joint Infection: A Preliminary Investigation.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2021 Jul 1;479(7):1458-1468. doi: 10.1097/CORR.0000000000001738. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2021. PMID: 33830953 Free PMC article.
-
Synovial C-Reactive Protein is a Useful Adjunct for Diagnosis of Periprosthetic Joint Infection.J Arthroplasty. 2022 Dec;37(12):2437-2443.e1. doi: 10.1016/j.arth.2022.06.016. Epub 2022 Jun 22. J Arthroplasty. 2022. PMID: 35750152 Review.
-
Reliability of d-Dimer Determination in Diagnosis of Peri-Prosthetic Joint Infection: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Surg Infect (Larchmt). 2021 May;22(4):374-382. doi: 10.1089/sur.2020.212. Epub 2020 Sep 8. Surg Infect (Larchmt). 2021. PMID: 32897817
References
-
- Abdelaziz H., Aljawabra A., Rossmann M., Tien C. S., Citak M., Klatte T. O., et al. . (2022). What is the impact of automated synovial cell counting on different aseptic causes and periprosthetic conditions associated with revision THA? Clin. Orthop Relat. Res. 480, 905–914. doi: 10.1097/CORR.0000000000002063 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Berthoud O., Coiffier G., Albert J. D., Gougeon-Jolivet A., Goussault C., Bendavid C., et al. . (2020). Performance of a new rapid diagnostic test the lactate/glucose ratio of synovial fluid for the diagnosis of septic arthritis. Joint Bone Spine 87, 343–350. doi: 10.1016/j.jbspin.2020.03.009 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Carli A. V., Abdelbary H., Ahmadzai N., Cheng W., Shea B., Hutton B., et al. . (2019). et al: diagnostic accuracy of serum, synovial, and tissue testing for chronic periprosthetic joint infection after hip and knee replacements: A systematic review. J. Bone Joint Surg. Am. 101, 635–649. doi: 10.2106/JBJS.18.00632 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Chen Y., Kang X., Tao J., Zhang Y., Ying C., Lin W. (2019). Reliability of synovial fluid alpha-defensin and leukocyte esterase in diagnosing periprosthetic joint infection (PJI): a systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Orthop Surg. Res. 14, 453. doi: 10.1186/s13018-019-1395-3 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous