Montelukast sodium combined with levocabastine nasal spray demonstrates high efficacy in treating pediatric allergic rhinitis
- PMID: 40384999
- PMCID: PMC12082512
- DOI: 10.62347/HYBG4442
Montelukast sodium combined with levocabastine nasal spray demonstrates high efficacy in treating pediatric allergic rhinitis
Abstract
Objectives: To investigate the efficacy and safety of montelukast sodium (MKS) combined with levocabastine (LEVO) nasal spray in treating pediatric allergic rhinitis and its impact on quality of life (AR).
Methods: A total of 125 pediatric AR patients, diagnosed between September 2022 and September 2024, were enrolled and divided into two groups. The research group (n = 65) received MKS plus LEVO nasal spray, while the control group (n = 60) received LEVO nasal spray alone. Treatment efficacy, safety (assessing xerostomia, headache, and gastrointestinal disturbances), and clinical symptom scores (rhinorrhea, sneezing, nasal obstruction, and nasal pruritus) were evaluated. Additionally, nasal cavity parameters (nasal resistance (NR), minimum cross-sectional area (mCSA), and nasal cavity volume (NCV)), serum inflammatory markers (IL-4, IL-8, IL-10), serum biochemical indices (total immunoglobulin E [TlgE], eosinophil count [EOS], eosinophil cationic protein [ECP]), and quality of life (Rhinoconjunctivitis Quality of Life Questionnaire [RQLQ]) were analyzed. Univariate and multivariate binary logistic regression analyses were conducted to identify factors influencing treatment outcomes.
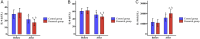
Results: The research group demonstrated significantly higher overall treatment efficacy than the control group (P<0.05), with a comparable safety profile (P>0.05). Post-treatment, clinical symptom scores, IL-4, IL-8, TlgE, EOS, ECP levels and RQLQ scores were significantly reduced in the research group compared to the control group (all P<0.05). Conversely, IL-10 levels were significantly higher in the research group (both P<0.05). Notably, passive secondhand smoke exposure, IL-10, EOS, and treatment modality were significantly associated with treatment efficacy (all P<0.05). Binary logistic regression identified passive secondhand smoke exposure (P = 0.035) and EOS (P = 0.036) as independent risk factors for treatment outcomes.
Conclusions: The combination of MKS and LEVO nasal spray demonstrates superior efficacy and safety in pediatric AR treatment, significantly improving patients' quality of life. Moreover, treatment failure is closely linked to passive secondhand smoke exposure and elevated EOS levels.
Keywords: Montelukast sodium; efficacy; levocabastine nasal spray; pediatric allergic rhinitis; quality of life; safety.
AJTR Copyright © 2025.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Randomized placebo-controlled trial comparing fluticasone aqueous nasal spray in mono-therapy, fluticasone plus cetirizine, fluticasone plus montelukast and cetirizine plus montelukast for seasonal allergic rhinitis.Clin Exp Allergy. 2004 Feb;34(2):259-67. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.2004.01877.x. Clin Exp Allergy. 2004. PMID: 14987306 Clinical Trial.
-
[Clinical evaluation of Montelukast plus Budesonide nasal spray and Desloratadine citrate disodium in treating moderate and severe persistent allergic rhinitis].Lin Chuang Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2015 Dec;29(23):2041-3. Lin Chuang Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2015. PMID: 27101674 Clinical Trial. Chinese.
-
A systematic review and meta-analysis of loratadine combined with montelukast for the treatment of allergic rhinitis.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Oct 17;14:1287320. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1287320. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37915414 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy and Safety of Montelukast+Levocetirizine Combination Therapy Compared to Montelukast Monotherapy for Allergic Rhinitis in Children.Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2024 Nov;16(6):652-667. doi: 10.4168/aair.2024.16.6.652. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2024. PMID: 39622689 Free PMC article.
-
Levocabastine. An update of its pharmacology, clinical efficacy and tolerability in the topical treatment of allergic rhinitis and conjunctivitis.Drugs. 1995 Dec;50(6):1032-49. doi: 10.2165/00003495-199550060-00009. Drugs. 1995. PMID: 8612470 Review.
References
-
- Hu Y, Luo H, Li J, Zhang R, Fu L, Ren Q, Chen Y, Huang X, Zhou Z, Yuan H, Tian L, Wang X. Immunofluorescent labeling in nasal mucosa tissue sections of allergic rhinitis rats via multicolor immunoassay. J Vis Exp. 2023 - PubMed
-
- Bernstein JA, Bernstein JS, Makol R, Ward S. Allergic rhinitis: a review. JAMA. 2024;331:866–877. - PubMed
-
- Zhang M, Ni JZ, Cheng L. Safety of intranasal corticosteroids for allergic rhinitis in children. Expert Opin Drug Saf. 2022;21:931–938. - PubMed
-
- Licari A, Magri P, De Silvestri A, Giannetti A, Indolfi C, Mori F, Marseglia GL, Peroni D. Epidemiology of allergic rhinitis in children: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2023;11:2547–2556. - PubMed
-
- Eremija J, Carr TF. Immunotherapy for asthma. Semin Respir Crit Care Med. 2022;43:709–719. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
