Fenofibrate mitigates the dysfunction of high glucose-driven human retinal microvascular endothelial cells by suppressing NLRP3 inflammasome
- PMID: 40385128
- PMCID: PMC12043296
- DOI: 10.18240/ijo.2025.05.04
Fenofibrate mitigates the dysfunction of high glucose-driven human retinal microvascular endothelial cells by suppressing NLRP3 inflammasome
Abstract
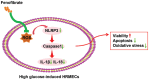
Aim: To determine the therapeutic benefits of fenofibrate (Feno) on the dysfunction of high glucose (HG)-induced human retinal microvascular endothelial cells (HRMECs) and to elucidate the underlying molecular mechanism.
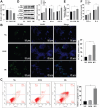
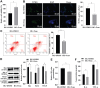
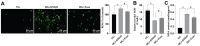
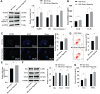
Methods: HRMEC dysfunction model was established by 48h glucose (30 mmol/L) treatment and treated with Feno/NOD-like receptor thermal protein domain associated protein 3 (NLRP3) inflammasome activator (Nigericin). Cell viability/apoptosis were assessed by cell counting kit-8 (CCK-8)/terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase-mediated dUTP-biotin nick end labeling assay (TUNEL) staining and flow cytometry assays. Levels of apoptosis- (Bcl-2-associated X protein, Bax/B-cell lymphoma 2, Bcl-2), vascular permeability-(vascular endothelial growth factor, VEGF) and inflammasome activation-related proteins (NLRP3/cleaved caspase-1/apoptosis-associated speck-like protein containing a CARD, ASC), as well as inflammatory factors (interleukin, IL-6/IL-1β/tumor necrosis factor, TNF-α/IL-18) were determined with Western blot/enzyme linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Cell permeability/reactive oxygen species (ROS) level/superoxide dismutase (SOD) activity/malondialdehyde (MDA) content were assessed by Evans blue staining/2',7'-dichlorodihydrofluorescein diacetate (DCFH-DA) fluorescent probe/SOD kit/MDA kit.
Results: HRMEC dysfunction was successfully induced by HG, evidenced by decreased viability (P<0.001), increased apoptosis (P<0.001), permeability (P<0.001), and inflammatory factor levels (P<0.001). Feno treatment significantly ameliorated HG-induced HRMEC dysfunction (P<0.01). Meanwhile, HG induction increased ROS production (P<0.001) and MDA content (P<0.001) in HRMECs, while reducing SOD activity (P<0.001), indicative of oxidative stress. This was, however, abolished by Feno (P<0.05). Moreover, Feno eliminated activation of NLRP3 inflammasomes (P<0.05) in HG-induced HRMECs. Strikingly, activation of NLRP3 inflammasomes partially averted the inhibition of Feno on HG-induced HRMEC dysfunction (P<0.05).
Conclusion: Feno represses oxidative stress and NLRP3 inflammasome activation, consequently alleviating HG-induced HRMEC dysfunction.
Keywords: NOD-like receptor thermal protein domain associated protein 3 inflammasomes; fenofibrate; high glucose; human retinal microvascular endothelial cells; oxidative stress.
International Journal of Ophthalmology Press.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: Shi Y, None; Chen HM, None; Liu AH, None; Li XR, None.
Figures
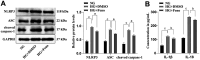
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
