Synergistic Inhibition of Colon Cancer Cell Proliferation via p53, Bax, and Bcl-2 Modulation by Curcumin and Plumbagin Combination
- PMID: 40385152
- PMCID: PMC12079253
- DOI: 10.1021/acsomega.5c01258
Synergistic Inhibition of Colon Cancer Cell Proliferation via p53, Bax, and Bcl-2 Modulation by Curcumin and Plumbagin Combination
Abstract
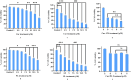
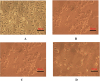
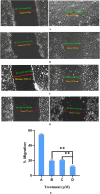
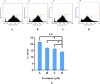
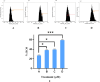
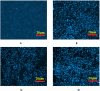
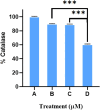
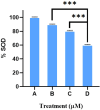
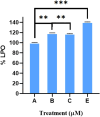
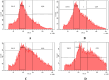
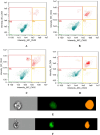
Cancer is a major contributor to global morbidity and mortality. Among the different forms of cancer, colorectal cancer (CRC) is the third most frequently diagnosed cancer in men and the second most common cancer type in women globally. We aimed to explore the possible synergistic anticancer potential of curcumin (Cur) and plumbagin (PL) in the human colon cancer cell line (HCT-116). The 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT)/cytotoxicity assay revealed IC50 values of 7.7 and 7.5 μM for Cur and PL, respectively, as a separate entity. However, the combined treatment of Cur + PL significantly enhanced the cancer cell growth inhibitory potential compared with solitary treatments with an IC50 value of 6.8 μM. The combined treatment also led to the induction of apoptosis by 41%, cell cycle arrest at the G2/M phase, while Bax and p53 genes were found to be upregulated and the Bcl-2 gene was downregulated compared to the untreated/solvent control. Furthermore, combined treatment elevated reactive oxygen species (ROS) production by 59% and resulted a decline in the mitochondrial membrane potential (MMP) compared to the control. Catalase and superoxide dismutase (SOD) activities were significantly reduced, leading to enhanced lipid peroxidation (LPO) and compromised membrane integrity, which were also confirmed by 4',6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI) + propoidium iodide (PI) staining were also noted. Our in vitro data were further supported by molecular docking, which showed a higher binding energy of the proteins (Bax, Bcl-2, and p53) with Cur + PL. Overall, our findings highlight the potent synergistic effects of the Cur and PL combination, which can be exploited as a combination therapy for CRC.
© 2025 The Authors. Published by American Chemical Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures

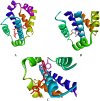

Similar articles
-
Curcumin chemo-sensitizes intrinsic apoptosis through ROS-mediated mitochondrial hyperpolarization and DNA damage in breast cancer cells.Cell Signal. 2025 Apr;128:111637. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2025.111637. Epub 2025 Feb 3. Cell Signal. 2025. PMID: 39909177
-
Plumbagin promotes mitochondrial mediated apoptosis in gefitinib sensitive and resistant A549 lung cancer cell line through enhancing reactive oxygen species generation.Mol Biol Rep. 2020 Jun;47(6):4155-4168. doi: 10.1007/s11033-020-05464-w. Epub 2020 May 22. Mol Biol Rep. 2020. PMID: 32444975
-
Boosting curcumin activity against human prostatic cancer PC3 cells by utilizing scorpion venom conjugated phytosomes as promising functionalized nanovesicles.Drug Deliv. 2022 Dec;29(1):807-820. doi: 10.1080/10717544.2022.2048133. Drug Deliv. 2022. PMID: 35266425 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-proliferative and apoptotic effect of gemini curcumin in p53-wild type and p53-mutant colorectal cancer cell lines.Int J Pharm. 2021 May 15;601:120592. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2021.120592. Epub 2021 Apr 20. Int J Pharm. 2021. PMID: 33857585
-
Curcumin suppresses colorectal cancer by induction of ferroptosis via regulation of p53 and solute carrier family 7 member 11/glutathione/glutathione peroxidase 4 signaling axis.Phytother Res. 2024 Aug;38(8):3954-3972. doi: 10.1002/ptr.8258. Epub 2024 Jun 4. Phytother Res. 2024. PMID: 38837315
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
