This is a preprint.
Mediating role of Interleukin-6 in the predictive association of diabetes with Hippocampus atrophy, Amyloid, Tau, and Neurofilament pathology at pre-clinical stages of diabetes-related cognitive impairment
- PMID: 40385439
- PMCID: PMC12083567
- DOI: 10.1101/2025.05.06.25327092
Mediating role of Interleukin-6 in the predictive association of diabetes with Hippocampus atrophy, Amyloid, Tau, and Neurofilament pathology at pre-clinical stages of diabetes-related cognitive impairment
Update in
-
Mediating role of Interleukin-6 in the predictive association of diabetes with Hippocampus atrophy, Amyloid, Tau, and Neurofilament pathology at pre-clinical stages of diabetes-related cognitive impairment.Brain Behav Immun Health. 2025 Jun 16;47:101031. doi: 10.1016/j.bbih.2025.101031. eCollection 2025 Aug. Brain Behav Immun Health. 2025. PMID: 40606939 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Introduction: Type-2 diabetes (T2DM) has been associated with higher dementia risks, but the mechanisms are still unclear, and there is increasing evidence of the role of cytokines. Interleukin-6 (IL-6) mediating effect has never been explored.
Methods: The study included a subset of 1,927 participants from the Health and Aging Brain Study: Healthy Disparities (HABS-HD) cohort with complete data. Cross-sectional and longitudinal analyses were performed. Associations were studied using multivariable linear, logistic, and mediation analysis with non-parametric bootstrapping.
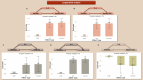
Results: T2DM and IL-6 were associated with worse executive function, Hippocampus atrophy, lower Aß42/Aß40 ratio, and higher Aß40, Aß42, total Tau, and NfL levels. IL-6 mediated 5% of the association of T2DM with Aß40 ([1.5%-10%], p-value<2×10-16), 4% with Aß42 ([0.7%-11%], p-value=0.014), 8% with TMT-B ([0.2%-35%], p-value=0.046), 11% with total Tau ([2.5%-40%], p-value=0.010), 5% with NfL ([1.6%-8%], p-value<2×10-16), and 12% hippocampus atrophy ([3%-49%], p-value=0.004). The results, except TMT-B, were replicated in the longitudinal analysis of long-lasting T2DM on non-previously diagnosed cognitive impairment.
Conclusions: The study captured a pre-clinical stage of the T2DM-dementia association. The mediating effect of IL-6 is a novelty that has to be further explored and accounted for in risk stratification and preventive measures, particularly in ethnic minorities.
Keywords: Cognition; aging; brain; cytokine; insulin resistance; neuroinflammation.
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations Conflicts of interest: The authors have no conflict of interest, neither financial nor non-financial.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Mediating role of Interleukin-6 in the predictive association of diabetes with Hippocampus atrophy, Amyloid, Tau, and Neurofilament pathology at pre-clinical stages of diabetes-related cognitive impairment.Brain Behav Immun Health. 2025 Jun 16;47:101031. doi: 10.1016/j.bbih.2025.101031. eCollection 2025 Aug. Brain Behav Immun Health. 2025. PMID: 40606939 Free PMC article.
-
CSF tau and the CSF tau/ABeta ratio for the diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease dementia and other dementias in people with mild cognitive impairment (MCI).Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Mar 22;3(3):CD010803. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010803.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 28328043 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy of nicergoline in dementia and other age associated forms of cognitive impairment.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2001;2001(4):CD003159. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003159. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2001. PMID: 11687175 Free PMC article.
-
Cholinesterase inhibitors for vascular dementia and other vascular cognitive impairments: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Feb 22;2(2):CD013306. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013306.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. PMID: 33704781 Free PMC article.
-
Folic acid with or without vitamin B12 for cognition and dementia.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2003;(4):CD004514. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD004514. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2003. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2008 Oct 08;(4):CD004514. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD004514.pub2. PMID: 14584018 Updated.
References
-
- van Sloten TT, Luchsinger JA, Launer LJ, Strachan M, Cukierman-Yaffe T, Gerstein HC, et al. Call for effective therapies for preventing dementia in people with type 2 diabetes. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2024;12(8):510–3. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
