This is a preprint.
Unravelling the molecular mechanisms causal to type 2 diabetes across global populations and disease-relevant tissues
- PMID: 40385441
- PMCID: PMC12083623
- DOI: 10.1101/2025.05.05.25326880
Unravelling the molecular mechanisms causal to type 2 diabetes across global populations and disease-relevant tissues
Update in
-
Unravelling the molecular mechanisms causal to type 2 diabetes across global populations and disease-relevant tissues.Nat Metab. 2026 Jan 27. doi: 10.1038/s42255-025-01444-1. Online ahead of print. Nat Metab. 2026. PMID: 41593238
Abstract
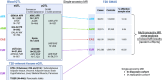
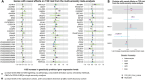
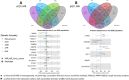
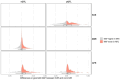
Type 2 diabetes (T2D) is a prevalent disease that arises from complex molecular mechanisms. Here, we leverage T2D multi-ancestry genetic associations to identify causal molecular mechanisms in an ancestry- and tissue-aware manner. Using two-sample Mendelian Randomization corroborated by colocalization across four global ancestries, we analyze 20,307 gene and 1,630 protein expression levels using blood-derived cis-quantitative trait loci (QTLs). We detect causal effects of genetically predicted levels of 335 genes and 46 proteins on T2D risk, with 16.4% and 50% replication in independent cohorts, respectively. Using gene expression cis-QTLs derived from seven T2D-relevant tissues, we identify causal links between the expression of 676 genes and T2D risk, including novel associations such as CPXM1, PTGES2 and FAM20B. Causal effects are mostly shared across ancestries, but highly heterogeneous across tissues. Our findings provide insights in cross-ancestry and tissue-informed multi-omics causal inference analysis approaches and demonstrate their power in uncovering molecular processes driving T2D.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
