Gen-miR-5 derived from Gentianella acuta inhibits PFKP to prevent fibroblast activation and alleviate myocardial fibrosis
- PMID: 40385478
- PMCID: PMC12081263
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1578877
Gen-miR-5 derived from Gentianella acuta inhibits PFKP to prevent fibroblast activation and alleviate myocardial fibrosis
Abstract
Introduction: Myocardial fibrosis (MF) is a key pathological change in heart failure, and lactate a product of glycolysis, is an important component affecting the process of MF. miRNAs derived from Gentianella acuta (G. acuta) have been shown to effectively treat cardiac remodeling. However, whether G. acuta-derived Gen-miR-5 can effectively improve MF remains to be elucidated. This study seeks to explore the pharmacological effects and underlying molecular mechanisms of Gen-miR-5 in the context of Angiotensin II (Ang II) -induced MF.
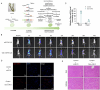
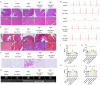
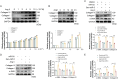
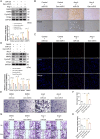
Methods: A mouse model of MF was established by subcutaneous infusion of Ang II using osmotic pumps, and then administration of Gen-miR-5 by injection. The effects of Gen-miR-5 in reducing MF and exerting cardioprotective actions were evaluated through pathological morphological analysis and echocardiography. The targeting effect of Gen-miR-5 on PFKP was assessed through dual-luciferase reporter gene assays. Cardiac fibroblasts (CFs) migration abilities were evaluated through wound healing assay and transwell assays. Additionally, the role of Gen-miR-5 in fibroblast activation was investigated using gain- and loss-of-function experiments, and immunofluorescence.
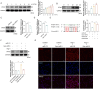
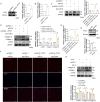
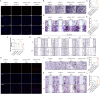
Results: This study identified six novel specific miRNAs in G. acuta, among which Gen-miR-5 can be absorbed by mice, stably exists in cardiac tissue, and targets the PFKP 3' UTR to exert cross-kingdom regulatory effects. PFKP, as a key rate-limiting enzyme in the glycolytic pathway, increases lactate accumulation and promotes the proliferation and migration of CFs, thereby facilitating the development of MF. In contrast, Gen-miR-5 alleviates MF by inhibiting this process.
Discussion: In conclusion, we have elucidated for the first time the pharmacological effects of Gen-miR-5, derived from G. acuta, in inhibiting MF. Gen-miR-5 exerts its cardioprotective effects by targeting and inhibiting the expression of the key glycolytic enzyme PFKP, induced by Ang II, regulating lactate metabolism in fibroblast, and preventing the transformation of fibroblasts into myofibroblasts, ultimately alleviating MF. This study demonstrates that Gen-miR-5 is a potential therapeutic agent for improving cardiac remodeling.
Keywords: PFKP; fibroblast activation; lactate; myocardial fibrosis; plant-derived miRNAs.
Copyright © 2025 Ge, Du, Liu, Wang, Li, Yang and Li.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Gentianella acuta-derived Gen-miR-1 suppresses myocardial fibrosis by targeting HAX1/HMG20A/Smads axis to attenuate inflammation in cardiac fibroblasts.Phytomedicine. 2023 Sep;118:154923. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2023.154923. Epub 2023 Jun 16. Phytomedicine. 2023. PMID: 37352750
-
Gentianella acuta improves TAC-induced cardiac remodelling by regulating the Notch and PI3K/Akt/FOXO1/3 pathways.Biomed Pharmacother. 2022 Oct;154:113564. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2022.113564. Epub 2022 Aug 19. Biomed Pharmacother. 2022. PMID: 35988427
-
Leonurine Attenuates Myocardial Fibrosis Through Upregulation of miR-29a-3p in Mice Post-myocardial Infarction.J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2021 Feb 1;77(2):189-199. doi: 10.1097/FJC.0000000000000957. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33235025
-
PFKP: More than phosphofructokinase.Adv Cancer Res. 2023;160:1-15. doi: 10.1016/bs.acr.2023.03.001. Epub 2023 Mar 30. Adv Cancer Res. 2023. PMID: 37704285 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Myocardial Fibrosis: Assessment, Quantification, Prognostic Signification, and Anti-Fibrosis Targets: A State-of-the-Art Review.J Cardiovasc Dev Dis. 2025 May 18;12(5):192. doi: 10.3390/jcdd12050192. J Cardiovasc Dev Dis. 2025. PMID: 40422963 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

