Low-dose statins restore innate immune response in breast cancer cells via suppression of mutant p53
- PMID: 40385487
- PMCID: PMC12081456
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1492305
Low-dose statins restore innate immune response in breast cancer cells via suppression of mutant p53
Abstract
Background: Breast cancer's high recurrence and treatment side effects demand safer, more effective therapies. Mutations in the critical TP53 gene, which normally prevents cancer, can instead promote it. This study explores if low-dose statins can curb mutant p53 activation in breast cancer's immune signaling, hindering tumor immune evasion.
Methods: The study used diverse breast cancer cell lines with varying p53 statuses. Techniques included Western blot, transfection, qRT-PCR, co-immunoprecipitation, nuclear fractionation, and immunohistochemistry. In vivo experiments used BALB/c mice, with bioinformatics analysis via cBioPortal.
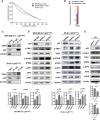
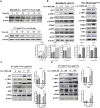
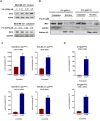
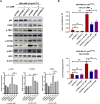
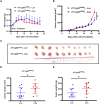
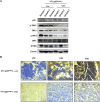
Results: The study found that suppressing mutant p53 restores innate immunity and enhances cancer treatment. Low-dose statins promoted IRF3 nuclear translocation by inhibiting mutant p53. Lovastatin treatment in vivo increased phosphorylated TBK1 and IRF3 levels and induced CD8+ T lymphocyte infiltration in tumors.
Conclusion: The findings suggest low-dose statins can enhance innate immunity in breast cancer by degrading mutant p53, offering new treatment possibilities. Caution is advised, and further research is needed to address limitations and provide solid evidence for clinical use.
Keywords: CGAS; STING; breast cancer; p53; statin.
Copyright © 2025 Wang, Shi, Liu, Zhang, Lin, Yang, Huang, Yang, Chu, Zheng and Ma.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Mutant p53 suppresses innate immune signaling to promote tumorigenesis.Cancer Cell. 2021 Apr 12;39(4):494-508.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.ccell.2021.01.003. Epub 2021 Feb 4. Cancer Cell. 2021. PMID: 33545063 Free PMC article.
-
Mutant p53R211* ameliorates inflammatory arthritis in AIA rats via inhibition of TBK1-IRF3 innate immune response.Inflamm Res. 2023 Dec;72(12):2199-2219. doi: 10.1007/s00011-023-01809-w. Epub 2023 Nov 8. Inflamm Res. 2023. PMID: 37935918 Free PMC article.
-
[Buzhong Yiqi Decoction alleviates immune injury of autoimmune thyroiditis in NOD.H-2~(h4)mice via c GAS-STING signaling pathway].Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2025 Apr;50(7):1872-1880. doi: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20241107.703. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2025. PMID: 40350879 Chinese.
-
p53 in breast cancer subtypes and new insights into response to chemotherapy.Breast. 2013 Aug;22 Suppl 2:S27-9. doi: 10.1016/j.breast.2013.07.005. Breast. 2013. PMID: 24074787 Review.
-
TP53 Mutation-Mediated Immune Evasion in Cancer: Mechanisms and Therapeutic Implications.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Sep 3;16(17):3069. doi: 10.3390/cancers16173069. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39272927 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Anderson K., Nelson C. H., Gong Q., Alani M., Tarnowski T., Othman A. A. (2022). Assessment of the effect of filgotinib on the pharmacokinetics of atorvastatin, pravastatin, and rosuvastatin in healthy adult participants. Clin. Pharmacol. Drug Dev. 11, 235–245. 10.1002/cpdd.1015 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

