Nanoemulsions Based Therapeutic Strategies: Enhancing Targeted Drug Delivery against Breast Cancer Cells
- PMID: 40385492
- PMCID: PMC12085896
- DOI: 10.2147/IJN.S488545
Nanoemulsions Based Therapeutic Strategies: Enhancing Targeted Drug Delivery against Breast Cancer Cells
Abstract
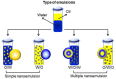
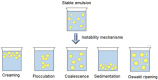
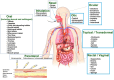
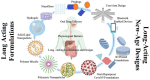
Nanoemulsions (NEs), colloidal systems of nanoscale droplets (~100 nm), have emerged as transformative tools in oncology due to their high surface area-to-volume ratio, tunable physicochemical properties, and capacity for targeted drug delivery. While NEs find applications across diverse fields, their urgency in breast cancer therapy stems from critical limitations of conventional treatments, including systemic toxicity, poor bioavailability, and multidrug resistance. Unlike traditional chemotherapeutics, NEs enable precise tumor targeting via passive mechanisms (eg, enhanced permeability and retention effect) and active strategies (eg, ligand-functionalized surfaces), significantly reducing off-target effects. Their ability to encapsulate hydrophobic drugs, improve solubility, and sustain controlled release enhances therapeutic efficacy while overcoming resistance mechanisms prevalent in aggressive breast cancer subtypes, such as triple-negative and HER2-positive tumors. This review comprehensively analyzes NE formulation techniques (eg, ultrasonication, phase inversion temperature, bubble bursting), stability optimization through surfactant dynamics, and predictive modeling of droplet behavior. A focal point is their role in modulating tumor microenvironments, inducing apoptosis, and inhibiting angiogenesis in preclinical breast cancer models. By spotlighting NE-driven advancements in drug accumulation, reduced relapse rates, and adaptable combination therapies, this article underscores their potential to revolutionize oncology. Future research must prioritize clinical translation, scalability, and multifunctional NE designs to address unmet needs in precision breast cancer treatment.
Keywords: breast cancer therapy; nanoemulsions; nanoscale droplets; targeted drug delivery; tumor microenvironment.
© 2025 Izadiyan et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The author(s) report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Surfactant-based drug delivery systems for cancer therapy: Advances, challenges, and future perspectives.Int J Pharm. 2025 Jun 30;679:125655. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2025.125655. Epub 2025 May 2. Int J Pharm. 2025. PMID: 40320019 Review.
-
Gelatin nanocarriers in oncology: A biocompatible strategy for targeted drug delivery.Int J Biol Macromol. 2025 May;310(Pt 1):143244. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2025.143244. Epub 2025 Apr 17. Int J Biol Macromol. 2025. PMID: 40250682 Review.
-
Anti-Netrin-1 decorated nanoparticles combined with chemotherapy for the treatment of triple-negative breast cancer.Biomater Adv. 2024 Jul;161:213881. doi: 10.1016/j.bioadv.2024.213881. Epub 2024 Apr 26. Biomater Adv. 2024. PMID: 38749213
-
Advancements in Solid Lipid Nanoparticles and Nanostructured Lipid Carriers for Breast Cancer Therapy.Curr Pharm Des. 2024;30(37):2922-2936. doi: 10.2174/0113816128319233240725103706. Curr Pharm Des. 2024. PMID: 39150028 Review.
-
Polyglutamic acid in cancer nanomedicine: Advances in multifunctional delivery platforms.Int J Pharm. 2025 May 15;676:125623. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2025.125623. Epub 2025 Apr 18. Int J Pharm. 2025. PMID: 40254191 Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

