Protective factors against oxidative stress in COPD: focus on Nrf2-dependent antioxidant gene expression
- PMID: 40385585
- PMCID: PMC12081257
- DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2025.1492256
Protective factors against oxidative stress in COPD: focus on Nrf2-dependent antioxidant gene expression
Abstract
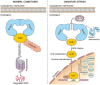
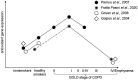
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) continues to be the world's primary cause of morbidity and mortality. The main mechanism driving the pathogenesis of COPD is oxidative stress. Antioxidant genes, regulated by the Nrf2/ARE signaling pathway, play a protective role against oxidative stress. Unfortunately, this pathway appears to be dysregulated in COPD, leading to decreased expression of antioxidant genes and persistent oxidative stress. We reviewed numerous studies measuring the expression of antioxidant genes in COPD. We also focused on developments in methods used to study gene expression in COPD over time, along with measuring antioxidant gene expression in various cell types, and the potential use of antioxidant gene expression as a predictor of COPD progression. And last but not least we discussed the association of cigarette smoke exposure with antioxidant gene expression together with antioxidant treatment in COPD. Understanding the altered expression of antioxidant genes in COPD could help in treating COPD, as well as predicting its progression.
Keywords: Nrf2/ARE signaling pathway; antioxidant gene expression; antioxidant treatment; antioxidants; chronic obstructive pulmonary disease; oxidative stress.
Copyright © 2025 Kominkova, Petrek and Navratilova.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The author(s) declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision.
Figures
References
-
- GOLD . (2025). Global initiative for chronic obstructive lung disease. Global strategy for the diagnosis, management, and prevention of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.
-
- Dheera DDD, Ralalage JRH. Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: Aetiology, pathology, physiology and outcome. Medicine. (2023) 51:737–41. doi: 10.1016/j.mpmed.2023.07.008 - DOI
-
- Hurst JR, Han MK, Singh B, Sharma S, Kaur G, de Nigris E, et al. Prognostic risk factors for moderate-to-severe exacerbations in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: a systematic literature review. Respir Res. (2022) 23:213. doi: 10.1186/s12931-022-02123-5, PMID: - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

