Successful management of Lomentospora prolificans septic arthritis and osteomyelitis in an immunocompetent child: A case report
- PMID: 40385599
- PMCID: PMC12084070
- DOI: 10.1016/j.mmcr.2025.100704
Successful management of Lomentospora prolificans septic arthritis and osteomyelitis in an immunocompetent child: A case report
Abstract
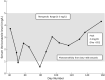
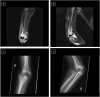
Available online We report a case of limb-threatening Lomentospora prolificans elbow infection in a 3-year-old immunocompetent boy following a closed fracture. Resolution of infection was achieved following combined aggressive debridement, combined antifungal therapy, voriconazole-loaded bone cement, and antiseptic joint irrigation. This highlights the need for early diagnosis and multi-modal surgical, medical and other novel adjunctive therapies in managing these difficult-to-treat infections. Increased research and improved access to novel antifungal drugs are essential to enhance treatment options for intrinsically multidrug-resistant fungal infections.
Keywords: Osteomyelitis septic arthritis Lomentospora prolificans voriconazole paediatric.
© 2025 The Authors. Published by Elsevier B.V. on behalf of International Society for Human and Animal Mycology.
Conflict of interest statement
There are none.
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization . first ed. WHO; Geneva: 2022. Fungal Priority Pathogens List to Guide Research, Development and Public Health Action.
-
- Hoenigl M., Salmanton-García J., Walsh T.J., Nucci M., Neoh C.F., Jenks J.D., et al. Global guideline for the diagnosis and management of rare mould infections: an initiative of the European confederation of medical Mycology in cooperation with the international society for human and animal Mycology and the American society for microbiology. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2021 Aug;21(8):e246–e257. - PubMed
-
- Seidel D., Hassler A., Salmanton-García J., Koehler P., Mellinghoff S.C., Carlesse F., et al. Invasive Scedosporium spp. and Lomentospora prolificans infections in pediatric patients: analysis of 55 cases from FungiScope® and the literature. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2020 Mar;92:114–122. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

