Intra-tumoural RAMP1+ B cells promote resistance to neoadjuvant anti-PD-1-based therapy in oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma
- PMID: 40385640
- PMCID: PMC12084762
- DOI: 10.1093/immadv/ltaf012
Intra-tumoural RAMP1+ B cells promote resistance to neoadjuvant anti-PD-1-based therapy in oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma
Abstract
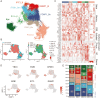
Introduction: The application of neoadjuvant immunotherapy in oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) reactivates anti-tumour immune responses and prolong postoperative survival. However, due to the heterogeneity of tumour microenvironment, limited patients have achieved pathological regression after treatment. The dual roles of B cells were recently highlighted in ESCC. The study aimed to investigate the role of B cell subclusters and the upstream signalling of B cell differentiation in ESCC resistant to immunotherapy.
Methods: Single-cell RNA sequencing was employed for ESCC specimens with distinct responses to neoadjuvant immunotherapy to map the landscape of intra-tumoural B cells.
Results: A novel subset of neuropeptide receptor, receptor activity-modifying protein 1 (RAMP1) positive B cells was revealed to accumulate in ESCC that is resistant to neoadjuvant immunotherapy. Stimulated by nociceptor neurons secreting calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP), RAMP1(+) B cells exhibit an immunosuppressive phenotype. The elevated secretion of immune-regulating cytokines by RAMP1(+) B cells blunts the cytotoxicity of Cluster of Differentiation (CD)8(+) T cell and leads to tumour immune evasion. A combination of RAMP1 blocker and anti-Programmed cell death protein (PD)-1 therapies synergistically reinvigorated anti-tumour immunity, reducing tumour progression in vitro.
Conclusion: The study suggests that RAMP1(+) B cells play a critical role in mediating resistance to neoadjuvant immunotherapy in ESCC. Targeting the CGRP-RAMP axis remodels B cells and enhance the efficacy of current immunotherapies, providing new strategies for overcoming treatment resistance.
Keywords: B cell; immunotherapy; neuroimmunology; regulation; suppression.
© The Author(s) 2025. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the British Society for Immunology.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Genomic profiling and associated B cell lineages delineate the efficacy of neoadjuvant anti-PD-1-based therapy in oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma.EBioMedicine. 2024 Feb;100:104971. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2024.104971. Epub 2024 Jan 19. EBioMedicine. 2024. PMID: 38244291 Free PMC article.
-
Single-cell profiling of response to neoadjuvant chemo-immunotherapy in surgically resectable esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.Genome Med. 2024 Apr 2;16(1):49. doi: 10.1186/s13073-024-01320-9. Genome Med. 2024. PMID: 38566201 Free PMC article.
-
Long noncoding RNA Regulating ImMune Escape regulates mixed lineage leukaemia protein-1-H3K4me3-mediated immune escape in oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma.Clin Transl Med. 2023 Sep;13(9):e1410. doi: 10.1002/ctm2.1410. Clin Transl Med. 2023. PMID: 37712124 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring novel immunotherapy in advanced esophageal squamous cell carcinoma: Is targeting TIGIT an answer?Esophagus. 2025 Apr;22(2):139-147. doi: 10.1007/s10388-024-01105-4. Epub 2025 Jan 23. Esophagus. 2025. PMID: 39847233 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Immune checkpoint inhibitors in the treatment of oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma: where are we and where are we going?Ther Adv Med Oncol. 2023 Aug 2;15:17588359231189420. doi: 10.1177/17588359231189420. eCollection 2023. Ther Adv Med Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37547447 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Xu J, Kato K, Raymond E. et al. Tislelizumab plus chemotherapy versus placebo plus chemotherapy as first-line treatment for advanced or metastatic oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma (RATIONALE-306): a global, randomised, placebo-controlled, phase 3 study. Lancet Oncol 2023; 24:483–95. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1470-2045(23)00108-0 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Yang Y, Zhu L, Cheng Y. et al. Three-arm phase II trial comparing camrelizumab plus chemotherapy versus camrelizumab plus chemoradiation versus chemoradiation as preoperative treatment for locally advanced esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (NICE-2 Study). BMC Cancer 2022; 22:506. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12885-022-09573-6 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Li C, Zhao S, Zheng Y. et al. Preoperative pembrolizumab combined with chemoradiotherapy for oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma (PALACE-1). Eur J Cancer 2021; 144:232–41. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejca.2020.11.039 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Li Q, Liu T, Ding Z.. Neoadjuvant immunotherapy for resectable esophageal cancer: a review. Front Immunol 2022; 13:1051841. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2022.1051841 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Cabrita R, Lauss M, Sanna A. et al. Tertiary lymphoid structures improve immunotherapy and survival in melanoma. Nature 2020; 577:561–5. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-019-1914-8 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
