Effects of Advance Care Planning on the Mental Health of Bereaved Families: A Systematic Review
- PMID: 40385767
- PMCID: PMC12084671
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.82403
Effects of Advance Care Planning on the Mental Health of Bereaved Families: A Systematic Review
Abstract
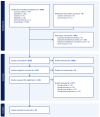
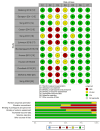
Decisions regarding end-of-life care are often made by surrogate decision makers, such as family members. These decisions can place a significant psychological burden on surrogates, especially when the patients' wishes are unclear. Advance care planning (ACP) is a patient-centered preconsultation process that is expected to improve the mental health of surrogate decision-makers. This study aimed to clarify the impact of ACP intervention on the mental health of bereaved families and verify its effectiveness. This review followed the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses guidelines. MEDLINE, EMBASE, PsycINFO, and Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials were searched for studies evaluating ACP interventions published up to 2024. Studies were independently selected by two researchers using the Covidence systematic review software (Veritas Health Innovation, Melbourne, Australia). The inclusion criteria were (i) studies evaluating the effectiveness of ACP interventions, (ⅱ) studies reporting bereaved mental health outcomes, and (ⅲ) randomized controlled trials (RCTs). Among the 2,025 studies initially identified, 12 RCTs were included. All interventions involved health professionals trained to facilitate ACP discussions before the patient died. Mental health was assessed using depression, anxiety, and posttraumatic stress disorder scales. The items for which significant differences were reported varied among the studies, but several studies reported effectiveness in treating depression in bereaved families. Furthermore, when baseline-adjusted results were included, ACP interventions reduced post-bereavement anxiety and stress experienced by families. In conclusion, depending on the targets and intervention methods, pre-death discussions may improve the mental health of bereaved families. Thus, ACP should be implemented to help bereaved families.
Keywords: advance care planning (acp); bereaved families; end-of-life care; mental health; surrogate decision-makers; systematic review.
Copyright © 2025, Tsubaki et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest: In compliance with the ICMJE uniform disclosure form, all authors declare the following: Payment/services info: The research, writing, and publication of this paper have been supported by the following grant: Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (grant number: JP21K17428). Financial relationships: All authors have declared that they have no financial relationships at present or within the previous three years with any organizations that might have an interest in the submitted work. Other relationships: All authors have declared that there are no other relationships or activities that could appear to have influenced the submitted work.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Effectiveness of an Advance Care Planning Intervention in Adults Receiving Dialysis and Their Families: A Cluster Randomized Clinical Trial.JAMA Netw Open. 2024 Jan 2;7(1):e2351511. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.51511. JAMA Netw Open. 2024. PMID: 38289604 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Advance care planning for adults with heart failure.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Feb 27;2(2):CD013022. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013022.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. PMID: 32104908 Free PMC article.
-
Advance care planning and end-of-life decision making in dialysis: a randomized controlled trial targeting patients and their surrogates.Am J Kidney Dis. 2015 Nov;66(5):813-22. doi: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2015.05.018. Epub 2015 Jun 30. Am J Kidney Dis. 2015. PMID: 26141307 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Experiences with and outcomes of Advance Care Planning in bereaved relatives of frail older patients: a mixed methods study.Age Ageing. 2019 Mar 1;48(2):299-306. doi: 10.1093/ageing/afy184. Age Ageing. 2019. PMID: 30615071 Clinical Trial.
-
The Effect of Advance Care Planning on Heart Failure: a Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.J Gen Intern Med. 2020 Mar;35(3):874-884. doi: 10.1007/s11606-019-05482-w. Epub 2019 Nov 12. J Gen Intern Med. 2020. PMID: 31720968 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Family surrogate decision-makers' perspectives in decision-making of patients with disorders of consciousness. Chen J, Zeng L, Liu X, Wu Q, Jiang J, Shi Y. Neuropsychol Rehabil. 2023;33:1582–1597. - PubMed
-
- The experiences and perspectives of family surrogate decision-makers: a systematic review of qualitative studies. Su Y, Yuki M, Hirayama K. Patient Educ Couns. 2020;103:1070–1081. - PubMed
-
- Family members' perceptions of surrogate decision-making in the intensive care unit: a systematic review. Sui W, Gong X, Qiao X, Zhang L, Cheng J, Dong J, Zhuang Y. Int J Nurs Stud. 2023;137:104391. - PubMed
-
- The effectiveness of interventions to meet family needs of critically ill patients in an adult intensive care unit: a systematic review update. Kynoch K, Chang A, Coyer F, McArdle A. JBI Database System Rev Implement Rep. 2016;14:181–234. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
