A Case of Low T1 Mapping Values in Myocardial Calcifications in a Patient With End-Stage Renal Disease
- PMID: 40385786
- PMCID: PMC12085066
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.82431
A Case of Low T1 Mapping Values in Myocardial Calcifications in a Patient With End-Stage Renal Disease
Abstract
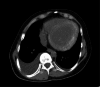
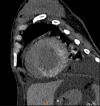
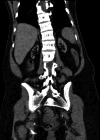
Cardiac MRI is the gold standard in diagnosing many cardiac pathologies. T1 mapping, a novel cardiac MRI sequence, provides precise assessment and characterization of myocardial tissue. Low T1 values have been reported in specific entities, including Fabry disease and iron overload. We report a case of decreased T1 values with diffuse myocardial calcifications in a 24-year-old female with end-stage renal disease. This case provides valuable new insights into T1 mapping, particularly regarding the association between myocardial calcifications and low T1 values, a connection that has only been reported in a single prior study.
Keywords: cardiac mri; diffuse myocardial calcifications; end-stage renal disease (esrd); t1 mapping; tissue characterization.
Copyright © 2025, Abdelmonem et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Human subjects: Consent for treatment and open access publication was obtained or waived by all participants in this study. Conflicts of interest: In compliance with the ICMJE uniform disclosure form, all authors declare the following: Payment/services info: All authors have declared that no financial support was received from any organization for the submitted work. Financial relationships: All authors have declared that they have no financial relationships at present or within the previous three years with any organizations that might have an interest in the submitted work. Other relationships: All authors have declared that there are no other relationships or activities that could appear to have influenced the submitted work.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Myocardial involvement in end-stage renal disease patients with anemia as assessed by cardiovascular magnetic resonance native T1 mapping: An observational study.Medicine (Baltimore). 2024 Nov 15;103(46):e39724. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000039724. Medicine (Baltimore). 2024. PMID: 39560547 Free PMC article.
-
Cardiac Intravoxel Incoherent Motion Diffusion-Weighted Magnetic Resonance Imaging With T1 Mapping to Assess Myocardial Perfusion and Fibrosis in Systemic Sclerosis: Association With Cardiac Events From a Prospective Cohort Study.Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020 Sep;72(9):1571-1580. doi: 10.1002/art.41308. Epub 2020 Aug 2. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020. PMID: 32379399
-
Myocardial T1 rho mapping of patients with end-stage renal disease and its comparison with T1 mapping and T2 mapping: A feasibility and reproducibility study.J Magn Reson Imaging. 2016 Sep;44(3):723-31. doi: 10.1002/jmri.25188. Epub 2016 Feb 18. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2016. PMID: 26889749
-
T1, T2 Mapping and Extracellular Volume Fraction (ECV): Application, Value and Further Perspectives in Myocardial Inflammation and Cardiomyopathies.Rofo. 2015 Sep;187(9):760-70. doi: 10.1055/s-0034-1399546. Epub 2015 Jun 22. Rofo. 2015. PMID: 26098250 Review.
-
T1 and T2 Mapping in Cardiology: "Mapping the Obscure Object of Desire".Cardiology. 2017;138(4):207-217. doi: 10.1159/000478901. Epub 2017 Aug 17. Cardiology. 2017. PMID: 28813699 Review.
References
-
- State of the art: clinical applications of cardiac T1 mapping. Schelbert EB, Messroghli DR. Radiology. 2016;278:658–676. - PubMed
-
- Clinical recommendations for cardiovascular magnetic resonance mapping of T1, T2, T2* and extracellular volume: a consensus statement by the Society for Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance (SCMR) endorsed by the European Association for Cardiovascular Imaging (EACVI) Messroghli DR, Moon JC, Ferreira VM, et al. J Cardiovasc Magn Reson. 2017;19:75. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
