A Questionnaire Study on Patient Perspectives of Sedation for Ophthalmic Procedures
- PMID: 40385789
- PMCID: PMC12083852
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.82385
A Questionnaire Study on Patient Perspectives of Sedation for Ophthalmic Procedures
Abstract
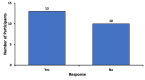
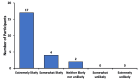
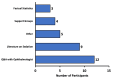
Introduction Ophthalmic procedures, such as cataract and refractive surgery, are prevalent in the United States and are often associated with significant preoperative anxiety among patients, which can impact patient comfort and surgical outcomes. Sedation is used in the vast majority of these procedures to reduce anxiety and improve patient cooperation. However, there is limited information on patient-reported experiences and perspectives. This study thus aimed to explore the opinions of patients on sedation for their eye procedures. Methods We administered an anonymous Qualtrics survey to gather data such as patient anxiety levels before and after sedation, patient satisfaction, potential side effects from sedatives, and perceived need for sedation in future procedures. The survey was posted in ophthalmology surgery clinics and online. Results Analysis of our filtered data found that the preoperative anxiety of patients significantly decreased after receiving sedation, with almost all participants in our survey recommending sedation for ophthalmic procedures to others. Many respondents suggested that resources such as question and answer (Q&A) sessions with ophthalmologists or literature would alleviate concerns about receiving sedation. Although a few mild side effects were self-reported from sedation, a majority of participants did not experience any side effects, and no severe side effects were noted. Conclusion These findings suggest that sedation for ophthalmic procedures is successful in reducing patient preoperative anxiety with minimal side effects. However, further research with larger, more diverse populations is warranted to confirm these results and guide future practices in patient care for ophthalmic surgeries.
Keywords: benzodiazepine; eye procedure; eye surgery; ophthalmology; patient opinion; sedation; survey.
Copyright © 2025, Awan et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Human subjects: Consent for treatment and open access publication was obtained or waived by all participants in this study. ACOM IRB issued approval Exempt. Animal subjects: All authors have confirmed that this study did not involve animal subjects or tissue. Conflicts of interest: In compliance with the ICMJE uniform disclosure form, all authors declare the following: Payment/services info: All authors have declared that no financial support was received from any organization for the submitted work. Financial relationships: All authors have declared that they have no financial relationships at present or within the previous three years with any organizations that might have an interest in the submitted work. Other relationships: All authors have declared that there are no other relationships or activities that could appear to have influenced the submitted work.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Patient Opinions and Side Effects Before and After General Anesthesia for Surgery.Cureus. 2024 Feb 7;16(2):e53755. doi: 10.7759/cureus.53755. eCollection 2024 Feb. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 38465100 Free PMC article.
-
Vesicoureteral Reflux.2024 Apr 30. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2024 Apr 30. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 33085409 Free Books & Documents.
-
Florida Controlled Substance Prescribing.2022 Oct 26. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2022 Oct 26. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 33428370 Free Books & Documents.
-
[The Assistant Doctors' Experience and Vocational Training Satisfaction in Ophthalmology in Bavaria: Outcomes of an Online Survey with Evaluation of the Vocational Training in Ophthalmic Surgery].Klin Monbl Augenheilkd. 2018 Dec;235(12):1398-1406. doi: 10.1055/s-0044-100614. Epub 2018 Apr 11. Klin Monbl Augenheilkd. 2018. PMID: 29642266 Review. German.
-
Conscious sedation during ophthalmic surgery under local anesthesia.Minerva Anestesiol. 2009 Apr;75(4):211-9. Epub 2008 Nov 6. Minerva Anestesiol. 2009. PMID: 18987568 Review.
References
-
- Epidemiology of primary ophthalmic procedures performed in the United States. Usmani B, Iftikhar M, Latif A, Shah SM. Can J Ophthalmol. 2019;54:727–734. - PubMed
-
- Peri-operative considerations for sedation-analgesia during cataract surgery: a narrative review. Kumar CM, Seet E, Eke T, Irwin MG, Joshi GP. Anaesthesia. 2019;74:1601–1610. - PubMed
-
- Conscious sedation during ophthalmic surgery under local anesthesia. Woo JH, Au Eong KG, Kumar CM. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/18987568/ Minerva Anestesiol. 2009;75:211–219. - PubMed
-
- Agents for sedation in ophthalmic surgery: a review of the pharmacodynamics and clinical applications. Loots H, Wiseman R. Curr Anaesth Crit Care. 2006;17:179–190.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
