Impact of fermentation on the processing and digestion characteristics of honeysuckle polyphenols by Lactobacillus acidophilus
- PMID: 40386218
- PMCID: PMC12083013
- DOI: 10.3389/fnut.2025.1570648
Impact of fermentation on the processing and digestion characteristics of honeysuckle polyphenols by Lactobacillus acidophilus
Abstract
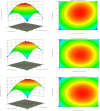
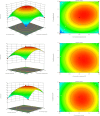
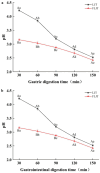
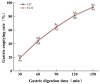
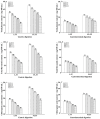
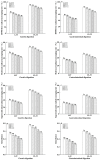
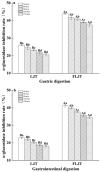
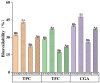
The technology and digestive characteristics of honeysuckle beverages fermented by Lactobacillus acidophilus were researched, the digestive characteristics were evaluated by simulating the gastrointestinal digestive system in vitro. The optimum conditions were as follows: fermentation temperature, 35°C; fermentation time, 19 h; and inoculation amount, 3%. Fermented honeysuckle beverages had greater antioxidant and α-glucosidase inhibition capacities than unfermented beverages after digestion. The bioavailabilities of total phenol, total flavonoids and chlorogenic acid in fermented honeysuckle liquid were 29.72, 21.80, and 36.93%, respectively, whereas those in unfermented honeysuckle liquid were 22.03, 17.28, and 25.67%, respectively. The pH of the fermented honeysuckle beverage remained relatively stable during storage at 4°C, with no significant change (p > 0.05). The number of viable bacteria decreased from 9.79 lg CFU/mL to 8.31 lg CFU/mL, and the sensory score and color decreased. This study provides a reference basis for the development of honeysuckle products and specific functional probiotic products.
Keywords: Lactobacillus acidophilus; digestion; fermentation; honeysuckle; processing.
Copyright © 2025 Dong, Shi, Zhang, Deng, Ge and Li.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Optimization of the fermentation process and antioxidant activity of mixed lactic acid bacteria for honeysuckle beverage.Front Microbiol. 2024 Apr 2;15:1364448. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1364448. eCollection 2024. Front Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38633692 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of different lactic acid bacteria fermentation on active substances and functional characteristics of honeysuckle liquid: analysis of metabolites of honeysuckle liquid based on metabolomics.Front Microbiol. 2025 May 26;16:1595351. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2025.1595351. eCollection 2025. Front Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40491835 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Lactobacillus (L. acidophilus NCIB1899, L. casei CRL 431, L. paracasei LP33) fermentation on free and bound polyphenolic, antioxidant activities in three Chenopodium quinoa cultivars.J Food Sci. 2023 Jun;88(6):2679-2692. doi: 10.1111/1750-3841.16604. Epub 2023 May 18. J Food Sci. 2023. PMID: 37199447
-
Probiotic fermented beverages based on acid whey.J Dairy Sci. 2019 Sep;102(9):7773-7780. doi: 10.3168/jds.2019-16385. Epub 2019 Jul 10. J Dairy Sci. 2019. PMID: 31301827
-
Physical, Chemical, Microbiological and Sensory Characteristics of a Probiotic Beverage Produced from Different Mixtures of Cow's Milk and Soy Beverage by Lactobacillus acidophilus La5 and Yoghurt Culture.Food Technol Biotechnol. 2019 Dec;57(4):461-471. doi: 10.17113/ftb.57.04.19.6344. Food Technol Biotechnol. 2019. PMID: 32123508 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kong DX, Li YQ, Bai M, Deng YL, Liang GX, Wu H. A comparative study of the dynamic accumulation of polyphenol components and the changes in their antioxidant activities in diploid and tetraploid Lonicera japonica. Plant Physiol Biochem. (2017) 112:87–96. doi: 10.1016/j.plaphy.2016.12.027, PMID: - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

