This is a preprint.
An integrated machine learning-based prognostic model in head and neck cancer using the systemic inflammatory response index and correlations with patient reported financial toxicity
- PMID: 40386418
- PMCID: PMC12083689
- DOI: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-6529613/v1
An integrated machine learning-based prognostic model in head and neck cancer using the systemic inflammatory response index and correlations with patient reported financial toxicity
Abstract
Objective: To investigate the prognostic utility of systemic inflammatory response index (SIRI) as a biological readout of stress associated immune modulation in head and neck cancer patients who underwent radiation therapy.
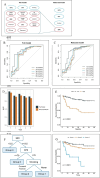
Methods: Random survival forest machine learning was used to model survival in 568 head and neck cancer patients. SIRI was calculated via pre-treatment bloodwork. Model validation was performed in an external cohort of 345 patients. Baseline financial toxicity (FT) and SIRI were studied in 638 patients.
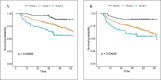
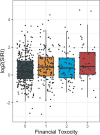
Results: Incorporation of SIRI (with performance status and smoking history) into a machine learning model identified three risk-groups that significantly stratified overall survival (p<0.0001,) and these findings were validated in the external validation cohort (p<0.001.) Increasing levels of FT were significantly associated with increasing SIRI levels. (p=0.001.).
Conclusions and relevance: An integrated machine learning model using clinical features was successfully developed and externally validated. SIRI was significantly associated with increasing FT. Our findings highlight the potential utility of SIRI as a biological marker of FT in head and neck cancer patients.
Keywords: Inflammation; lymphocyte; monocyte; neutrophil; squamous cell carcinoma.
Conflict of interest statement
Additional Declarations: There is NO Competing Interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The systemic inflammation response index predicts the survival of patients with clinical T1-2N0 oral squamous cell carcinoma.Oral Dis. 2022 Apr;28(3):600-610. doi: 10.1111/odi.13782. Epub 2021 Feb 9. Oral Dis. 2022. PMID: 33486833
-
Assessment of Preoperative Systemic Inflammation Response Index in Surgically Treated Young Head and Neck Cancer Patients Under 40.Ear Nose Throat J. 2025 May 6:1455613251338940. doi: 10.1177/01455613251338940. Online ahead of print. Ear Nose Throat J. 2025. PMID: 40327049
-
Prognostic capacity of Systemic Inflammation Response Index (SIRI) in patients with head and neck squamous cell carcinoma.Head Neck. 2020 Feb;42(2):336-343. doi: 10.1002/hed.26010. Epub 2019 Nov 21. Head Neck. 2020. PMID: 31750591
-
Machine learning consensus clustering for inflammatory subtype analysis in stroke and its impact on mortality risk: a study based on NHANES (1999-2018).Front Neurol. 2025 Apr 10;16:1562247. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2025.1562247. eCollection 2025. Front Neurol. 2025. PMID: 40276469 Free PMC article.
-
Body Mass Index Alters the Predictive Value of the Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio and Systemic Inflammation Response Index in Laryngeal Squamous Cell Carcinoma Patients.Nutr Cancer. 2022;74(4):1261-1269. doi: 10.1080/01635581.2021.1952447. Epub 2021 Jul 19. Nutr Cancer. 2022. PMID: 34278900
References
-
- Hajdu SI. Greco-Roman thought about cancer. Cancer. 2004;100(10):2048–2051. - PubMed
-
- Eckerling A, Ricon-Becker I, Sorski L, Sandbank E, Ben-Eliyahu S. Stress and cancer: mechanisms, significance and future directions. Nat Rev Cancer. 2021;21(12):767–785. - PubMed
-
- Sandi C, Haller J. Stress and the social brain: behavioural effects and neurobiological mechanisms. Nature Reviews Neuroscience. 2015;16(5):290–304. - PubMed
-
- Davis JM, Albert JD, Tracy KJ, et al. Increased neutrophil mobilization and decreased chemotaxis during cortisol and epinephrine infusions. J Trauma. 1991;31(6):725–731; discussion 731–722. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

