The contribution of social determinants of health to long-term outcomes following traumatic brain injury
- PMID: 40386445
- PMCID: PMC12084076
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ssmph.2025.101795
The contribution of social determinants of health to long-term outcomes following traumatic brain injury
Abstract
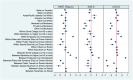
Social Determinants of Health (SDoH) are a significant factor in health outcomes for both acute and chronic health conditions, but systematic research related to outcomes from traumatic brain injury (TBI) has been limited. This study explores the relationship between individual and neighborhood-level SDoH and TBI outcomes to understand the extent of their influence on long-term recovery. Hybrid panel models that decompose time-varying predictors into between- and within-person effects were used to examine the relationships between SDoH and participation in the community, life satisfaction, and global functioning for persons with moderate to severe TBI one to 30 years post-injury. Participants were 9263 persons, distributed nationally, who received inpatient rehabilitation for TBI and enrolled in the TBI Model Systems longitudinal study. Individual-level SDoH included sex, race/ethnicity, education, employment, insurance, primary means of transportation, and rurality. The Social Vulnerability Index (SVI) was used as an indicator of neighborhood disadvantage. Results indicated that neighborhood-level SDoH accounted for differences in outcomes between individuals but not due to change in a given individual's neighborhood. These findings were robust to the inclusion of numerous individual-level SDoH, which were also associated with the outcomes. Individual-level SDoH accounted for differences in outcomes both between individuals and with change in a given individual's status. Among four thematic subscales constituting the SVI, the socio-economic status subscale was consistently associated with all three outcomes.
Keywords: Neighborhood disadvantage; Social determinants of health; Traumatic brain injury.
© 2025 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
None of the authors have financial or personal relationships with other people or organizations that could inappropriately influence or bias this work and thus have nothing to declare.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Exploring the Social Determinants of Health and Health Disparities in Traumatic Brain Injury: A Scoping Review.Brain Sci. 2023 Apr 23;13(5):707. doi: 10.3390/brainsci13050707. Brain Sci. 2023. PMID: 37239178 Free PMC article.
-
Association of Social Determinants of Health With Brain MRI Outcomes in Individuals With Pediatric Onset Multiple Sclerosis.Neurology. 2024 Dec 24;103(12):e210140. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000210140. Epub 2024 Nov 27. Neurology. 2024. PMID: 39602667
-
Are Commonly Used Geographically Based Social Determinant of Health Indices in Orthopaedic Surgery Research Correlated With Each Other and With PROMIS Global-10 Physical and Mental Health Scores?Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2024 Apr 1;482(4):604-614. doi: 10.1097/CORR.0000000000002896. Epub 2023 Oct 26. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2024. PMID: 37882798 Free PMC article.
-
Social Determinants of Health and Racial Disparities in Cardiac Events in Breast Cancer.J Natl Compr Canc Netw. 2023 Jul;21(7):705-714.e17. doi: 10.6004/jnccn.2023.7023. J Natl Compr Canc Netw. 2023. PMID: 37433439
-
Association of neighborhood-level social determinants of health with psychosocial distress in patients newly diagnosed with lung cancer.Cancer Rep (Hoboken). 2022 Nov;5(11):e1734. doi: 10.1002/cnr2.1734. Epub 2022 Oct 17. Cancer Rep (Hoboken). 2022. PMID: 36250328 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Arango-Lasprilla J.C., Ketchum J.M., Lewis A.N., Krch D., Gary K.W., Dodd B.A. Racial and ethnic disparities in employment outcomes for persons with traumatic brain injury: A longitudinal investigation 1-5 years after injury. PM & R: The Journal of Injury, Function, and Rehabilitation. 2011;3(12):1083–1091. doi: 10.1016/j.pmrj.2011.05.023. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Arango-Lasprilla J.C., Ketchum J.M., Williams K., Kreutzer J.S., Marquez de la Plata C.D., O'Neil-Pirozzi T.M., et al. Racial differences in employment outcomes after traumatic brain injury. Archives of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation. 2008;89(5):988–995. doi: 10.1016/j.apmr.2008.02.012. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

