KCNC3 as a prognostic indicator and a predictive marker for immunotherapy in colorectal cancer
- PMID: 40386598
- PMCID: PMC12078811
- DOI: 10.21037/jgo-24-718
KCNC3 as a prognostic indicator and a predictive marker for immunotherapy in colorectal cancer
Abstract
Background: Colorectal cancer (CRC) is a heterogeneous disease that is associated with several genetic or somatic mutations. Cancer immunotherapy has become a novel and revolutionary method of treatment for patients with advanced tumors. However, effective biomarkers that can reflect the response of CRC patients to immunotherapy have still not been identified. Our study aimed to explore the expression and functional role of KCNC3 in CRC.
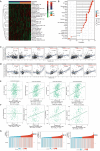
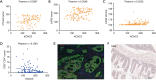
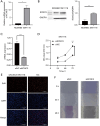
Methods: The correlation between KCNC3 expression levels and CRC progression was explored and validated using data from The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) and patient's samples from the Affiliated Hospital of Nantong University. Univariate and multivariate Cox regression models were developed to determine the predictive value of KCNC3 on the prognosis and immune activation of patients with CRC. We predicted the immunotherapy response in both the high and low KCNC3 expression subgroups. Finally, we confirmed that KCNC3 promotes the proliferation and invasion of colon cancer cells.
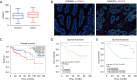
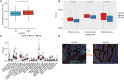
Results: In this study, data from TCGA database and clinical patient parameters showed that high KCNC3 expression was associated with tumor immune infiltration and poor prognosis of CRC. KCNC3 expression was positively correlated with the infiltration levels of CD4+ cells, regulatory T cells (Tregs), and myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSCs), which contributed to the formation of an immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment (TME). The high expression of KCNC3 was accompanied by the upregulation of immune checkpoint molecules, including PDCD1, LAG3, FOXP3, and CTLA4, which stimulated tumor cells to evade immune surveillance. In vitro experiment, KCNC3 knockdown inhibited the growth and metastasis of SW1116 cells.
Conclusions: This study demonstrated that the high expression of KCNC3 contributes to the growth and invasion of CRC and confers with immunosuppressive microenvironment that can promote tumor progression and can be used to predict the poor clinical outcome of CRC patients.
Keywords: KCNC3; colorectal cancer (CRC); prognosis; tumor immune microenvironment.
Copyright © 2025 AME Publishing Company. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at https://jgo.amegroups.com/article/view/10.21037/jgo-24-718/coif). The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures

References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
