Budesonide/glycopyrronium/formoterol fumarate co-suspension metered dose inhaler relieves cough after lobectomy: a randomized controlled study
- PMID: 40386713
- PMCID: PMC12082204
- DOI: 10.21037/tlcr-24-905
Budesonide/glycopyrronium/formoterol fumarate co-suspension metered dose inhaler relieves cough after lobectomy: a randomized controlled study
Abstract
Background: Cough after pulmonary resection (CAP) has emerged as a prevalent complication. However, existing treatment protocols for CAP lack standardization. The components of the budesonide/glycopyrronium/formoterol fumarate co-suspension metered dose inhaler (BGF MDI) have been consistently documented for their effectiveness in cough management. Consequently, we initiated this clinical trial to evaluate the efficacy and safety of BGF MDI in mitigating CAP.
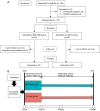
Methods: Enrolled participants exhibited no pre-existing cough before undergoing lobectomy. The patients were randomly assigned in a 1:1 ratio to either the BGF MDI group or the Control group. The BGF MDI group received BGF MDI for 14 consecutive days postoperatively; each participant in both groups underwent continuous follow-up for 60 days. Cough severity, duration, and cough-related quality of life were evaluated. The primary endpoints were focused on the occurrence of obvious CAP lasting ≥14 days.
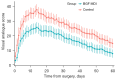
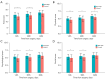
Results: Finally, 51 patients in the BGF MDI group and 52 patients in the Control group were included in the analysis after accounting for dropout. The BGF MDI group demonstrated a reduction in the incidence of obvious CAP lasting ≥14 days (13.7% vs. 40.4%). The cough-related quality of life for the BGF MDI group on the 14th and 30th days after surgery was higher. Three participants in the BGF MDI group reported palpitations, with no other complications noted.
Conclusions: BGF MDI has shown efficacy and safety in reducing CAP severity and duration. Using BGF MDI after lobectomy helps to alleviate cough symptoms and speed up postoperative recovery.
Trial registration: Clinicaltrials.gov. Clinical Trial Registry Number: NCT05472350.
Keywords: Lobectomy; inhalation therapy; life of quality; postoperative cough.
Copyright © 2025 AME Publishing Company. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at https://tlcr.amegroups.com/article/view/10.21037/tlcr-24-905/coif). The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Pharmacokinetics of budesonide/glycopyrrolate/formoterol fumarate metered dose inhaler formulated using co-suspension delivery technology after single and chronic dosing in patients with COPD.Pulm Pharmacol Ther. 2020 Feb;60:101873. doi: 10.1016/j.pupt.2019.101873. Epub 2019 Dec 10. Pulm Pharmacol Ther. 2020. PMID: 31841699 Clinical Trial.
-
The pharmacokinetics of three doses of budesonide/glycopyrronium/formoterol fumarate dihydrate metered dose inhaler compared with active controls: A Phase I randomized, single-dose, crossover study in healthy adults.Pulm Pharmacol Ther. 2018 Jun;50:11-18. doi: 10.1016/j.pupt.2018.03.001. Epub 2018 Mar 13. Pulm Pharmacol Ther. 2018. PMID: 29544728 Clinical Trial.
-
Pharmacokinetics and Tolerability of Budesonide/Glycopyrronium/Formoterol Fumarate Dihydrate and Glycopyrronium/Formoterol Fumarate Dihydrate Metered Dose Inhalers in Healthy Chinese Adults: A Randomized, Double-blind, Parallel-group Study.Clin Ther. 2019 May;41(5):897-909.e1. doi: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2019.03.007. Epub 2019 Apr 11. Clin Ther. 2019. PMID: 30982547 Clinical Trial.
-
Budesonide/Glycopyrrolate/Formoterol Fumarate Co-suspension Metered Dose Inhaler: A Triple Therapy for the Treatment of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease.Ann Pharmacother. 2022 May;56(5):582-591. doi: 10.1177/10600280211038353. Epub 2021 Aug 12. Ann Pharmacother. 2022. PMID: 34382422 Review.
-
Consistent Pulmonary Drug Delivery with Whole Lung Deposition Using the Aerosphere Inhaler: A Review of the Evidence.Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2021 Jan 18;16:113-124. doi: 10.2147/COPD.S274846. eCollection 2021. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2021. PMID: 33500616 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
