Predictive value of the monocyte-to-high-density lipoprotein ratio in the prognosis of non-small cell lung cancer patients after surgery
- PMID: 40386725
- PMCID: PMC12082247
- DOI: 10.21037/tlcr-2025-171
Predictive value of the monocyte-to-high-density lipoprotein ratio in the prognosis of non-small cell lung cancer patients after surgery
Abstract
Background: Due to the poor prognosis of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients, precise and reliable biomarkers are urgently needed to predict the prognosis in NSCLC patients after radical lung surgery. Hence, this study sought to investigate the correlation between the monocyte-to-high-density lipoprotein ratio (MHR) and overall survival (OS) in NSCLC patients after surgery.
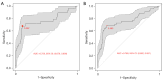
Methods: This retrospective study analyzed clinical data, including MHR, from NSCLC patients undergoing radical surgery. OS was calculated to evaluate the prognosis of the NSCLC patients. The association between the MHR and OS was analyzed. A receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve analysis was conducted to evaluate the 3- and 5-year predictive value of the MHR for prognosis after surgery.
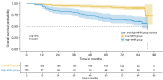
Results: In total, 256 patients were enrolled in this study. All patients had a follow-up for more than 5 years. The prognosis of the patients with a higher MHR (>0.3) was worse than that of the patients with a lower MHR (≤0.3) (P<0.001). The univariate Cox survival analysis showed that the MHR, surgery time, tumor (pT) stage, lymph node (pN) stage, and sex were all significantly associated with the risk of death in patients with NSCLC. The multivariate Cox survival analysis showed that the MHR [hazard ratio (HR) =24.837, 95% confidence interval (CI): 7.265-84.911], T stage, N stage, and surgery time were prognostic factors for NSCLC patients after surgery. The stratified analysis, which excluded patients with tumors in situ, showed that the MHR (HR =27.097, 95% CI: 8.081-90.877), surgery time, and pN stage significantly increased the risk of death in NSCLC patients. The area under the ROC curve (AUCROC) values of the MHR in predicting the 3- and 5-year survival of the NSCLC patients after surgery were 0.758 and 0.760, respectively.
Conclusions: The MHR was found to be an independent predictor of OS in NSCLC patients after radical surgery. Early monitoring and reducing the MHR may be of great significance in preventing disease recurrence and improving patient prognosis.
Keywords: Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC); monocyte-to-high-density lipoprotein ratio (MHR); overall survival (OS); prognosis; radical surgery.
Copyright © 2025 AME Publishing Company. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at https://tlcr.amegroups.com/article/view/10.21037/tlcr-2025-171/coif). The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures

References
-
- Rami-Porta R, Nishimura KK, Giroux DJ, et al. The International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer Lung Cancer Staging Project: Proposals for Revision of the TNM Stage Groups in the Forthcoming (Ninth) Edition of the TNM Classification for Lung Cancer. J Thorac Oncol 2024;19:1007-27. 10.1016/j.jtho.2024.02.011 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
