Recent advances of chimeric antigen receptor T-cell therapy for acute myeloid leukemia
- PMID: 40386773
- PMCID: PMC12081463
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1572407
Recent advances of chimeric antigen receptor T-cell therapy for acute myeloid leukemia
Abstract
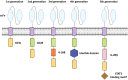
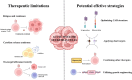
Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) is a heterogeneously primary hematopoietic neoplasm characterized by uncontrolled proliferation of immature myeloid cells, which is characterized with poor outcomes. Despite tremendous advances in the treatment paradigm of AML in the past several decades, the cure and prognosis remain unfavorable. More effective treatments are therefore needed to improve the clinical outcomes. Among newly emerging immunotherapies, chimeric antigen receptor (CAR)-T cell immunotherapy is an exceedingly promising approach that has remarkably improved the overall survival for patients with AML. However, current CAR-T cell therapy for AML faces numerous significant challenges such as the identification of truly AML-specific surface antigens, the on-target/off-tumor toxicity, and the immunosuppressive microenvironment of AML. In order to conquer these limitations, novel strategies to advance CAR-T therapy are urgently needed. In this comprehensive review, we summarize the current status of immunotherapy, especially CAR-T cell therapy, highlight the outcomes of current trials and the limitations of CAR-T immunotherapy, hopefully to provide novel insights into the future directions of CAR-T cells in AML.
Keywords: acute myeloid leukemia; adoptive cell therapy; chimeric antigen receptor T cell; immunosuppressive microenvironment; immunotherapy.
Copyright © 2025 Liu, Wang, Wang, Deng, Hu, Mei and Luo.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

