Incidence, characteristics and risk factors of tigecycline-induced hypoglycaemia: a retrospective study from the real world
- PMID: 40386810
- PMCID: PMC12084673
- DOI: 10.1093/jacamr/dlaf076
Incidence, characteristics and risk factors of tigecycline-induced hypoglycaemia: a retrospective study from the real world
Erratum in
-
Correction to: Incidence, characteristics and risk factors of tigecycline-induced hypoglycaemia: a retrospective study from the real world.JAC Antimicrob Resist. 2025 Jun 16;7(3):dlaf111. doi: 10.1093/jacamr/dlaf111. eCollection 2025 Jun. JAC Antimicrob Resist. 2025. PMID: 40524865 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Objectives: Tigecycline is widely used in clinic because of its broad spectrum of activity including activity against drug-resistance Gram-positive and -negative microorganisms. Hypoglycaemia is a rare but potentially fatal side effect during treatment with tigecycline. At present, data on tigecycline-induced hypoglycaemia are scarce, and there is a paucity of research summarizing the clinical characteristics and incidence rate of this uncommon adverse effect of tigecycline. The purpose of this study was to assess clinical characteristics and risk factors of tigecycline-associated hypoglycaemia.
Method: We performed this retrospective single-centre study of inpatients with tigecycline-induced hypoglycaemia in China between 2018 and 2024. Clinical data were achieved by review of medical records, and patients who met the inclusion criteria but did not develop hypoglycaemia were assigned as controls.
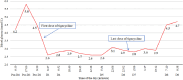
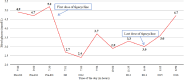
Results: We finally identified 14 patients with tigecycline-induced hypoglycaemia. The incidence rate of hypoglycaemia was 1.52% (14/922) in the study population. Tigecycline-induced hypoglycaemia can happen in patients with or without diabetes and develop independent of insulin or antidiabetic drugs. For patients of tigecycline-related hypoglycaemia, intravenous dextrose was effective in the restoration of euglycemia.
Conclusions: Health professional should be aware of the potential hypoglycaemia risk and monitor blood glucose level during treatment with tigecycline. For patients developing hypoglycaemia, the blood glucose monitoring should be careful and continuous even after tigecycline withdrawal.
© The Author(s) 2025. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of British Society for Antimicrobial Chemotherapy.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Tigecycline and Hypoglycemia, When and How?J Pharm Technol. 2024 Feb;40(1):37-44. doi: 10.1177/87551225231211737. Epub 2023 Nov 18. J Pharm Technol. 2024. PMID: 38318259 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Real-World Data of Tigecycline-Associated Drug-Induced Liver Injury Among Patients in China: A 3-year Retrospective Study as Assessed by the Updated RUCAM.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Nov 2;12:761167. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.761167. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34795591 Free PMC article.
-
(Ultra-)long-acting insulin analogues versus NPH insulin (human isophane insulin) for adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Nov 9;11(11):CD005613. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD005613.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. PMID: 33166419 Free PMC article.
-
Nursing and midwifery management of hypoglycaemia in healthy term neonates.Int J Evid Based Healthc. 2005 Aug;3(7):169-205. doi: 10.1111/j.1479-6988.2005.00025.x. Int J Evid Based Healthc. 2005. PMID: 21631748
-
Inpatient hypoglycaemia: understanding who is at risk.Diabetologia. 2020 Jul;63(7):1299-1304. doi: 10.1007/s00125-020-05139-y. Epub 2020 Apr 17. Diabetologia. 2020. PMID: 32300821 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous