Neural state changes during movie watching relate to episodic memory in younger and older adults
- PMID: 40386868
- PMCID: PMC12086427
- DOI: 10.1093/cercor/bhaf114
Neural state changes during movie watching relate to episodic memory in younger and older adults
Abstract
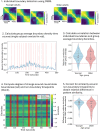
Event segmentation is a key feature underlying the ability to remember real-life occurrences. At the neural level, event boundaries have been shown to align with boundaries between neural states-stable patterns of brain activity maintained over time. These neural states provide a valuable window into the neural underpinnings of event perception. To investigate how neural state boundaries relate to memory across the lifespan, we used the data-driven Greedy State Boundary Search method to implicitly identify neural state changes in younger and older adults' electroencephalography data during movie watching. Memory for the movie was tested and related to (1) neural state correspondence across individuals and (2) the degree to which the pattern of activity changes at boundaries. Neural state boundaries significantly aligned across people, but did not differ with age nor relate to memory. The degree of change at neural state boundaries also did not differ with age, but was positively related to memory for the movie. These findings suggest that age differences in the perception of naturalistic events may be less pronounced than previously thought, at least when measured implicitly, and that greater distinction between successive neural states relates to better memory for one's experiences regardless of age.
Keywords: EEG; aging; episodic memory; event segmentation; neural states.
© The Author(s) 2025. Published by Oxford University Press.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Rapid Memory Reactivation at Movie Event Boundaries Promotes Episodic Encoding.J Neurosci. 2019 Oct 23;39(43):8538-8548. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0360-19.2019. Epub 2019 Sep 13. J Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 31519818 Free PMC article.
-
Looking the same, but remembering differently: Preserved eye-movement synchrony with age during movie watching.Psychol Aging. 2021 Aug;36(5):604-615. doi: 10.1037/pag0000615. Epub 2021 Jul 22. Psychol Aging. 2021. PMID: 34291964
-
Brain-environment alignment during movie watching predicts fluid intelligence and affective function in adulthood.Neuroimage. 2021 Sep;238:118177. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2021.118177. Epub 2021 May 18. Neuroimage. 2021. PMID: 34020016 Free PMC article.
-
Toward an integrative account of internal and external determinants of event segmentation.Psychon Bull Rev. 2024 Apr;31(2):484-506. doi: 10.3758/s13423-023-02375-2. Epub 2023 Sep 12. Psychon Bull Rev. 2024. PMID: 37698807 Review.
-
Boundaries Shape Cognitive Representations of Spaces and Events.Trends Cogn Sci. 2018 Jul;22(7):637-650. doi: 10.1016/j.tics.2018.03.013. Epub 2018 Apr 26. Trends Cogn Sci. 2018. PMID: 29706557 Review.
References
-
- Ataseven N, Ünver N, Günseli E. 2023. How does divided attention hinder different stages of episodic memory retrieval? Curr Res Behav Sci. 5:100139. 10.1016/j.crbeha.2023.100139. - DOI
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

