A Ketol-Acid Reductoisomerase Inhibitor That Has Antituberculosis and Herbicidal Activity
- PMID: 40386891
- PMCID: PMC12202844
- DOI: 10.1002/chem.202501158
A Ketol-Acid Reductoisomerase Inhibitor That Has Antituberculosis and Herbicidal Activity
Abstract
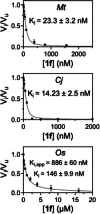
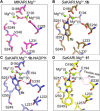
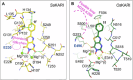
Ketol-acid reductoisomerase (KARI) is a target for the development of new biocidal agents. This is based on its essential role in branched chain amino acid biosynthesis in plants and microorganisms, and its absence in animals. The lack of success in developing KARI inhibitors as biocides may be because the inhibitors assessed to date compete directly with the substrate, 2-acetolactate (AL). As a result, effectiveness diminishes when AL accumulates in cells. Furthermore, as these inhibitors are slow binding, an organism could avoid growth slowdown by increasing KARI production. Here, we show a pyrimidinedione, 1f is a competitive but time-dependent inhibitor of AL and NADPH for Mycobacterium tuberculosis (Mt) KARI (Ki = 23.3 nM). A crystal structure of this compound bound to the MtKARI homolog from Staphylococcus aureus (Sa), SaKARI, illustrates this dual competition. In contrast, for Oryza sativa KARI, no time-dependent inhibition by 1f is observed, though it inhibits AL competitively (146 nM) and NADPH uncompetitively. Despite differences in inhibition properties, 1f has an MIC of 12.7 µm for MtH37Rv and inhibits Brassica campestris growth by 63% at 10 mg mL-1. Therefore, KARI inhibitors that are competitive for NADPH and show no time-dependent inhibition have excellent potential as biocides.
Keywords: Ketol‐acid reductoisomerase; crystal structure; drug discovery; herbicide discovery; inhibitor.
© 2025 The Author(s). Chemistry – A European Journal published by Wiley‐VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures












References
-
- Lopez M. J., Mohiuddin S. S., in StatPearls [Internet], StatPearls Publishing, Florida: 2023.
-
- Levitt G., US Patent , 1978, US4127405.
-
- Fletcher J. S., Pfleeger T. G., Ratsch H. C., Environ. Sci. Technol. 1993, 27, 2250. - PubMed
-
- Stidham M. A., Weed Sci. 1991, 39, 428.
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

