Hypoxia Inhibitor Improves Iodine Uptake Disorder in Thyroid Cancer Through the hsa_circ_0023990/miR-448/DNMT1/NIS Axis
- PMID: 40386902
- PMCID: PMC12317399
- DOI: 10.1111/cas.70102
Hypoxia Inhibitor Improves Iodine Uptake Disorder in Thyroid Cancer Through the hsa_circ_0023990/miR-448/DNMT1/NIS Axis
Abstract
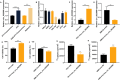
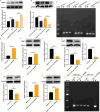
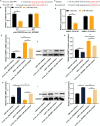
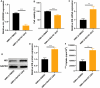
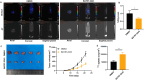
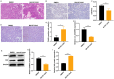
This research seeks to investigate how hypoxia inhibitors enhance iodine uptake in thyroid cancer cells. Clinical samples were gathered and assessed for hsa_circ_0023990, DNMT1, NIS, and their promoter methylation levels using RT-PCR, western blot, and methylation-specific PCR (MSP) techniques. The study involved examining the impact and mechanism of hsa_circ_0023990 on iodine uptake in differentiated thyroid carcinoma (DTC) cells through genetic manipulation. Luciferase reporter gene experiments were conducted to validate the interaction between hsa_circ_0023990, DNMT1, and miR-448. Xenograft tumors were established in nude mice for in vivo validation. The results showed that hsa_circ_0023990 was notably elevated in DTC and RAIR-DTC tissues. It was found that hsa_circ_0023990 could modulate NIS promoter methylation via the miR-448/DNMT1 signaling pathway, thereby influencing NIS expression. Hypoxia inhibitors effectively suppressed hsa_circ_0023990 expression in DTC cells, leading to increased NIS expression and enhanced iodine uptake. Subcutaneous transplantation experiments in animals further confirmed that hypoxia inhibitors could boost iodine absorption in tumor tissue and inhibit tumor growth through the hsa_circ_0023990/miR-448/DNMT1/NIS signaling axis. In conclusion, hypoxia inhibitors ameliorate iodine uptake dysfunction in thyroid cancer by acting on the hsa_circ_0023990/miR-448/DNMT1/NIS signaling pathway.
Keywords: NIS; hsa_circ_0023990; hypoxia inhibitor; iodine uptake disorder; thyroid cancer.
© 2025 The Author(s). Cancer Science published by John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd on behalf of Japanese Cancer Association.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Hsa_circ_0088036 promotes tumorigenesis and chemotherapy resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma via the miR-140-3p/KIF2A axis.Histol Histopathol. 2025 Aug;40(8):1239-1251. doi: 10.14670/HH-18-849. Epub 2024 Nov 19. Histol Histopathol. 2025. PMID: 39587911
-
Hsa_circ_0001640 inactivation of the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway by targeting the MiR-942-5p/PTEN axis to inhibit the progression of non-small cell lung cancer.Exp Cell Res. 2025 Jul 15;450(2):114673. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2025.114673. Epub 2025 Jul 12. Exp Cell Res. 2025. PMID: 40659239
-
Hsa_circ_0000119 promoted ovarian cancer development via enhancing the methylation of CDH13 by sponging miR-142-5p.J Biochem Mol Toxicol. 2023 Mar;37(3):e23264. doi: 10.1002/jbt.23264. Epub 2022 Dec 8. J Biochem Mol Toxicol. 2023. PMID: 36482494
-
circ-NOLC1 inhibits the development of cervical cancer by regulating miR-330-5p-PALM signaling axis.Hereditas. 2025 Jun 18;162(1):108. doi: 10.1186/s41065-025-00478-5. Hereditas. 2025. PMID: 40533863 Free PMC article.
-
Circular RNA circLIFR suppresses papillary thyroid cancer progression by modulating the miR-429/TIMP2 axis.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2024 Jun 25;150(6):323. doi: 10.1007/s00432-024-05839-7. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38914806 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Shen H., Zhu R., Liu Y., et al., “Radioiodine‐Refractory Differentiated Thyroid Cancer: Molecular Mechanisms and Therapeutic Strategies for Radioiodine Resistance,” Drug Resistance Updates 72 (2024): 101013. - PubMed
-
- Durante C., Haddy N., Baudin E., et al., “Long‐Term Outcome of 444 Patients With Distant Metastases From Papillary and Follicular Thyroid Carcinoma: Benefits and Limits of Radioiodine Therapy,” Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism 91 (2006): 2892–2899. - PubMed
-
- Zhang Q., Wu L., Liu S. Z., et al., “hsa_circ_0023990 Promotes Tumor Growth and Glycolysis in Dedifferentiated TC via Targeting miR‐485‐5p/FOXM1 Axis,” Endocrinology 162 (2021): bqab172. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

