Characterization of genome-wide transpositions induced by colistin exposure in multi-drug-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae
- PMID: 40387400
- PMCID: PMC12217459
- DOI: 10.1128/aac.01574-24
Characterization of genome-wide transpositions induced by colistin exposure in multi-drug-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae
Abstract
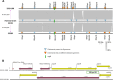
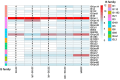
Colistin is one of the last-line antibiotics against multi-drug-resistant (MDR) gram-negative pathogens, such as Klebsiella pneumoniae. Using long-read sequencing, we observed remarkable genome-wide transposition events in MDR K. pneumoniae exposed to colistin in patients receiving treatment for respiratory infections or as part of selective decolonization strategies and further confirmed these on in vitro selection experiments. These data add yet another dimension to the role of antibiotics in mediating specific processes in bacteria beyond antibiotic resistance.CLINICAL TRIALSThis study is registered with ClinicalTrials.gov as NCT02208154.
Keywords: antibiotic resistance; colistin; insertion sequence elements; muti-drug resistant Klebsiella penumoniae.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Matheeussen V, Xavier BB, Mermans I, De Weerdt A, Lammens C, Goossens H, Jansens H, Malhotra-Kumar S. 2019. Emergence of colistin resistance during treatment of recurrent pneumonia caused by carbapenemase producing Klebsiella pneumoniae. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis 94:407–409. doi: 10.1016/j.diagmicrobio.2019.02.014 - DOI - PubMed
-
- WHO . 2018. Critically important antimicrobials for human medicine
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

