Development and Characterization of κ-Carrageenan-Based Edible Films Enriched With Resveratrol or Quercetin for Shelf-Life Extension of Goat Meat Burger Patties
- PMID: 40387509
- PMCID: PMC12087530
- DOI: 10.1111/1750-3841.70277
Development and Characterization of κ-Carrageenan-Based Edible Films Enriched With Resveratrol or Quercetin for Shelf-Life Extension of Goat Meat Burger Patties
Abstract
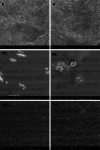
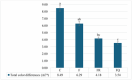
This study aimed to develop κ-carrageenan-based edible films enriched with resveratrol or quercetin and evaluate their potential in extending the shelf life and preserving the quality of goat meat burger patties during 14 days of storage at 4°C. The quercetin film solution exhibited greater antioxidant capacity than the resveratrol-containing film, as indicated by higher total phenolic content (389.00 ± 0.42 mg GAE/g), DPPH inhibition (91.85 ± 0.06%), and FRAP values (545.08 ± 0.37 µmol Fe2⁺/L) (p < 0.05). Incorporation of either compound decreased L* values and increased b* values (p < 0.05); resveratrol reduced opacity, whereas quercetin enhanced it (p < 0.05). No inhibition zones were observed against Listeria monocytogenes, Escherichia coli, Staphylococcus aureus, or Salmonella Typhimurium (p > 0.05). SEM micrographs showed that both compounds improved the homogeneity of the film matrix. The chemical composition and water activity of the patties were not significantly affected by the treatment, storage day, or their interaction (p > 0.05). However, patties coated with the quercetin films had a lower pH (pH 6.18 ± 0.01) than the control (pH 6.27 ± 0.03) (p < 0.05) and retained their initial color better. Additionally, quercetin effectively delayed lipid oxidation (21.98 ± 1.94 µmol MDA/kg) and inhibited microbial growth, maintaining TMAB counts below 10 CFU/g by Day 14 (p < 0.05). Overall, quercetin-containing κ-carrageenan films demonstrated promising technological and preservative properties, offering a sustainable alternative to conventional packaging for heat-treated ready-to-eat meat products. Future research should explore strategies such as controlled release, encapsulation, and synergistic bioactive combinations to further enhance efficacy.
Keywords: burger patty; edible film; goat meat; quercetin; resveratrol; shelf life; κ‐carrageenan.
© 2025 The Author(s). Journal of Food Science published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of Institute of Food Technologists.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Materialization of novel composite bio-based active edible film functionalized with essential oils on antimicrobial and antioxidative aspect of chicken nuggets during extended storage.J Food Sci. 2020 Sep;85(9):2857-2865. doi: 10.1111/1750-3841.15365. Epub 2020 Aug 18. J Food Sci. 2020. PMID: 32812228
-
Sustainable gelatin-kappa carrageenan active packaging with Mekwiya date seeds to enhance goat meat quality and shelf life.Int J Biol Macromol. 2024 Nov;279(Pt 2):135285. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2024.135285. Epub 2024 Sep 2. Int J Biol Macromol. 2024. PMID: 39233172
-
Effect of Edible Onion (Allium cepa L.) Film on Quality, Sensory Properties and Shelf Life of Beef Burger Patties.Molecules. 2021 Nov 27;26(23):7202. doi: 10.3390/molecules26237202. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 34885783 Free PMC article.
-
New opportunities and advances in quercetin-added functional packaging films for sustainable packaging applications: a mini-review.Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2024;64(23):8464-8479. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2023.2200553. Epub 2023 Apr 19. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2024. PMID: 37074182 Review.
-
Application of Nanotechnology to Develop Carrageenan-based Films and Coatings as Carriers for Essential Oils.Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2025;26(7):972-981. doi: 10.2174/0113892010287269240222054020. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2025. PMID: 38441010 Review.
References
-
- Abdalbeygi, S. , Aminzare M., and Hassanzad Azar H.. 2022. “Chitosan Edible Coating Incorporated With Resveratrol and Satureja Bachtiarica Essential Oil as Natural Active Packaging: In Vitro Antibacterial and Antioxidant Properties, and Its Impact on the Shelf Life of Fresh Chicken Fillet and Growth of Inoculated Escherichia coli O157:H7.” International Journal of Food Engineering 18, no. 10‐11: 701–715. 10.1515/ijfe-2022-0138. - DOI
-
- Ansarian, E. , Aminzare M., Azar H. H., Mehrasbi M. R., and Bimakr M.. 2022. “Nanoemulsion‐Based Basil Seed Gum Edible Film Containing Resveratrol and Clove Essential Oil: In Vitro Antioxidant Properties and Its Effect on Oxidative Stability and Sensory Characteristic of Camel Meat During Refrigeration Storage.” Meat Science 185: 108716. 10.1016/j.meatsci.2021.108716. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Arcan, I. , and Yemenicioğlu A.. 2011. “Incorporating Phenolic Compounds Opens a New Perspective to Use Zein Films as Flexible Bioactive Packaging Materials.” Food Research International 44, no. 2: 550–556. 10.1016/j.foodres.2010.11.034. - DOI
-
- Association of Official Analytical Chemists (AOAC) International . 1990. Protein (Crude) in Animal Feed. Dumas Method. 15th ed.
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

