Activation of HTR2B Suppresses Osteosarcoma Progression through the STAT1-NLRP3 Inflammasome Pathway and Promotes OASL1+ Macrophage Production to Enhance Antitumor Immunity
- PMID: 40387572
- PMCID: PMC12362726
- DOI: 10.1002/advs.202415276
Activation of HTR2B Suppresses Osteosarcoma Progression through the STAT1-NLRP3 Inflammasome Pathway and Promotes OASL1+ Macrophage Production to Enhance Antitumor Immunity
Abstract
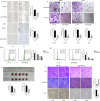
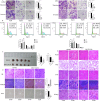
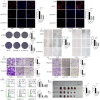
Osteosarcoma is a primary malignant bone tumor originating from mesenchymal tissue, and associated with poor prognosis. The 5-hydroxytryptamine receptor 2B (HTR2B), a receptor for serotonin, is known to play a role in the progression of multiple tumors. This study aims to explore the potential roles of HTR2B in osteosarcoma progression. HTR2B expression is analyzed using the TARGET, GEO databases, and osteosarcoma tissue samples in the hospital. Lentivirus and agonist BW-723C86 are employed to assess HTR2B overexpression effects in osteosarcoma cell lines. Transcriptome sequencing analysis and single-cell sequencing are performed to identify potential downstream molecules and signaling pathways, and the changes in tumor immune microenvironment. The investigation demonstrates that HTR2B is downregulated in osteosarcoma tissues, and correlates with poorer survival outcomes. Upregulating HTR2B through lentiviral-mediated gene delivery or the agonist BW-723C86, resulted in a marked suppression of osteosarcoma cell progression via the STAT1-NLRP3 inflammasome pathway. Single-cell sequencing of CD45+ cells reveals that HTR2B activation enhances the production of OASL1+ macrophages, contributing to the observed enhancement of antitumor immunity. These findings propose HTR2B as a novel therapeutic target for treating osteosarcoma, offering a dual mechanism of action that directly impedes tumor cell proliferation and augments the host immune response.
Keywords: HTR2B; OASL1+ macrophage; STAT1‐NLRP3 inflammasome; activation; osteosarcoma.
© 2025 The Author(s). Advanced Science published by Wiley‐VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures









References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 82072963/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 82103513/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 82303898/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 20224Y0136/Youth Projects for Clinical Research of Shanghai Municipal Health Commission
- 2023YJXYSC001/Program for Research-oriented Physician of Shanghai Tenth People's Hospital
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
