Site-to-site mutational dissection of fission yeast cohesin reveals its dynamics
- PMID: 40388360
- PMCID: PMC12239626
- DOI: 10.1093/g3journal/jkaf111
Site-to-site mutational dissection of fission yeast cohesin reveals its dynamics
Abstract
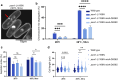
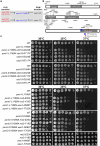
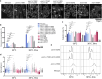
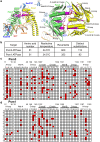
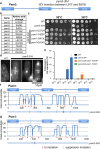
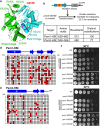
Cohesin is a heteropentameric protein complex that holds sister chromatids together from S phase to anaphase. Its 2 structural maintenance of chromosome subunits form a heterodimer, consisting of an ATPase head domain and a hinge domain connected by long coiled coils. Kleisin subunit associates with the head. Here, using Schizosaccharomyces pombe, we genetically dissected cohesin dynamics based on the relationship between the mutations causing temperature-sensitive and their suppressor mutations. First, we identified suppressor mutations that could rescue the lethality caused by cohesin ATPase mutations. Mutations in the DNA-binding domain of cohesin loader Mis4, or in cell-cycle genes encoding MBF transcription factor complex or Wee1 kinase, rescued both Psm1 and Psm3 ATPase mutants. Then, we performed targeted mutagenesis in both ATPase domains for single-amino-acid substitutions that can rescue the lethality of a kleisin ts mutant at restrictive temperature. Comparison of mutations obtained in Psm1 and Psm3 ATPase domains revealed that analogous mutations in the 2 ATPase domains were frequently observed. Last, suppressors of a coiled-coil mutation were mapped in coiled coils, indicating that proper folding of coiled coils is critical for cohesin functions. Suppressors of a hinge interface mutation are frequently located at the other hinge interface, indicating that the 2 cohesin hinge interfaces work collaboratively in hinge-hinge interactions. Overall, genetic dissection of the relationship between cohesin lethal mutations and their suppressor mutations reflects cohesin dynamics in vivo.
Keywords: cell cycle; chromosome segregation; cohesin; fission yeast; suppressor screen.
© The Author(s) 2025. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of The Genetics Society of America.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest: The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Suppressor mutation analysis combined with 3D modeling explains cohesin's capacity to hold and release DNA.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018 May 22;115(21):E4833-E4842. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1803564115. Epub 2018 May 7. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018. PMID: 29735656 Free PMC article.
-
Suppressor screening reveals common kleisin-hinge interaction in condensin and cohesin, but different modes of regulation.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019 May 28;116(22):10889-10898. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1902699116. Epub 2019 May 9. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019. PMID: 31072933 Free PMC article.
-
Cohesin ATPase activities regulate DNA binding and coiled-coil configuration.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2022 Aug 16;119(33):e2208004119. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2208004119. Epub 2022 Aug 8. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2022. PMID: 35939705 Free PMC article.
-
Cohesin mutations in acute myeloid leukemia.Leukemia. 2024 Nov;38(11):2318-2328. doi: 10.1038/s41375-024-02406-4. Epub 2024 Sep 9. Leukemia. 2024. PMID: 39251741 Review.
-
Prognosis of adults and children following a first unprovoked seizure.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023 Jan 23;1(1):CD013847. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013847.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023. PMID: 36688481 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
