Evolution and classification of Ser/Thr phosphatase PP2C family in bacteria: Sequence conservation, structures, domain distribution
- PMID: 40388423
- PMCID: PMC12088040
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0322880
Evolution and classification of Ser/Thr phosphatase PP2C family in bacteria: Sequence conservation, structures, domain distribution
Abstract
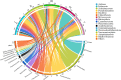
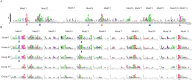
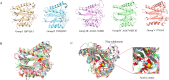
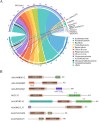
Serine/threonine kinases (STKs) and serine/threonine phosphatases (STPs) are widely present across various organisms and play crucial roles in regulating cellular processes such as growth, proliferation, signal transduction, and other physiological functions. Recent research has increasingly focused on the regulation of STKs and STPs in bacteria. STKs have been well studied, identified and characterized in a variety of bacterial species. However, the role of STPs in bacteria remains less understood, and the number of proteins characterized is limited. It has been found that most of the STPs characterized in bacteria were Mg2+/Mn2+ dependent 2C protein phosphatases (PP2Cs), but the evolutionary relationship and taxonomic distribution of bacterial PP2C phosphatases were still not fully elucidated. In this study, we utilized bacterial PP2C phosphatase sequences from the InterPro database to perform a phylogenetic analysis, categorizing the family into five groups. Based on this classification, we examined the evolutionary relationships, species distribution, sequence and structural variations, and domain distribution characteristics of bacterial PP2C phosphatases. Our analysis uncovered evidence of a common evolutionary origin for bacterial PP2C phosphatases. These findings advance the understanding of PP2C phosphatases, offering valuable insights for future functional studies of bacterial serine/threonine phosphatases and aiding in the design of targeted therapeutics for pathogenic bacteria.
Copyright: © 2025 Li et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

