Value of SOFA score, APACHE II score, and WBC count for mortality risk assessment in septic patients: A retrospective study
- PMID: 40388734
- PMCID: PMC12091671
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000042464
Value of SOFA score, APACHE II score, and WBC count for mortality risk assessment in septic patients: A retrospective study
Abstract
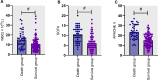
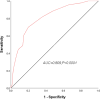
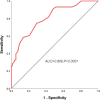
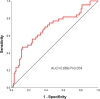
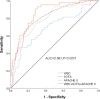
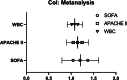
Sepsis is characterized by rapid onset, swift progression, and poor prognosis. Delay in early recognition and treatment may easily escalate to septic shock, resulting in a markedly high mortality rate. Early prognosis assessment holds significant value in enhancing the clinical outcomes of septic patients. The sequential organ failure assessment (SOFA) score and acute physiology and chronic health evaluation II (APACHE II) score are commonly utilized clinical tools for assessing patients' conditions, while white blood cell (WBC) count is frequently employed to evaluate the inflammatory status of the body. The study aimed to investigate the prognostic value of SOFA score, APACHE II score, and WBC count in assessing the risk of mortality in septic patients, providing valuable insights for improving the prognosis of septic patients. In this retrospective study, 139 patients diagnosed with sepsis in our hospital from January 2021 to December 2023 were selected as the study subjects. Clinical outcomes of the patients were collected through a 28-day follow-up period, and patients were categorized into the survival group (n = 96) and the death group (n = 43). The value of SOFA score, APACHE II score, and WBC count for the mortality risk assessment in septic patients was calculated by plotting ROC curves, and the risk factors for mortality in septic patients were analyzed. The AUC of SOFA score was 0.809 (95% CI = 0.734-0.871, P < .0001) for predicting the mortality risk of sepsis. The AUC of APACHE score was 0.806 (95% CI = 0.729-0.884, P < .0001) for predicting the mortality risk of sepsis. The AUC of WBC count was 0.689 (95% CI = 0.591-0.788, P = .004) for predicting the mortality risk of sepsis. The AUC of combined detection was 0.861 (95% CI = 0.792-0.914, P < .0001) for predicting the mortality risk of sepsis. Univariate analysis revealed that SOFA, APACHE II, and WBC were correlated with mortality in septic patients (P < .05). Patients with sepsis demonstrate significant elevations in WBC count, SOFA, and APACHE II scores. The combined application of these indicators holds considerable value in predicting the mortality outcomes of septic patients. Accordingly, clinical treatment plans can be adjusted based on these aforementioned indicators to ameliorate the prognosis of septic patients.
Keywords: APACHE II score; SOFA score; WBC count; mortality outcome; predictive value; sepsis.
Copyright © 2025 the Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no funding and conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Early lactate/albumin ratio combined with quick sequential organ failure assessment for predicting the prognosis of sepsis caused by community-acquired pneumonia in the emergency department].Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2025 Feb;37(2):118-122. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn121430-20240709-00577. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2025. PMID: 40017357 Chinese.
-
[Combined prognostic value of serum lactic acid, procalcitonin and severity score for short-term prognosis of septic shock patients].Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2021 Mar;33(3):281-285. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn121430-20201113-00715. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2021. PMID: 33834968 Chinese.
-
[Clinical characteristics and prognosis of acute gastrointestinal injury in patients with sepsis-associated acute respiratory distress syndrome].Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2024 Jun;36(6):591-596. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn121430-20240118-00063. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2024. PMID: 38991957 Chinese.
-
[Lactic acid, lactate clearance and procalcitonin in assessing the severity and predicting prognosis in sepsis].Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2020 Apr;32(4):449-453. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn121430-20200129-00086. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2020. PMID: 32527351 Chinese.
-
[The value of coagulation indicators combined with sequential organ failure assessment in assessing disease severity and prognosis of elderly patients with sepsis].Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2024 Nov;36(11):1133-1139. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn121430-20240424-00374. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2024. PMID: 39697016 Chinese.
References
-
- Xia H, Wang F, Wang M, et al. . Maresin1 ameliorates acute lung injury induced by sepsis through regulating Th17/Treg balance. Life Sci. 2020;254:117773. - PubMed
-
- Zou Q, Yang M, Yu M, Liu C. Influences of regulation of miR-126 on inflammation,Th17/Treg subpopulation differentiation, and lymphocyte apoptosis through caspase signaling pathway in sepsis. Inflammation. 2020;43:2287–300. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

