Reduction of artifacts from contrast media in spectral-detector CT by combined use of virtual monoenergetic images and orthopedic metal-artifact-reduction algorithm
- PMID: 40388764
- PMCID: PMC12091650
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000042370
Reduction of artifacts from contrast media in spectral-detector CT by combined use of virtual monoenergetic images and orthopedic metal-artifact-reduction algorithm
Abstract
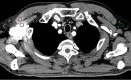
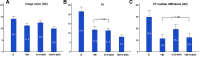
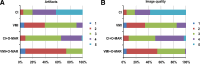
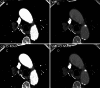
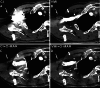
This study assesses the artifacts reduction caused by contrast media (CM) in the subclavian and axillary veins in dual-layer spectral-detector CT using virtual monoenergetic images (VMI) and orthopedic metal-artifact-reduction (O-MAR) algorithm. A total of 61 nonconsecutive patients who underwent enhanced chest CT examinations were enrolled in the present study. Conventional images (CI), VMI, CI with O-MAR algorithm (CI + O-MAR), and VMI with O-MAR algorithm (VMI + O-MAR) were reconstructed using the same arterial CT dataset. The VMI and VMI + O-MAR images were reconstructed at 130 keV. Subjective image quality assessment was performed in terms of degree of artifacts and overall image quality using the Likert-scale. The differences in image noise, artifact index (AI) and CT number difference were compared among the 4 reconstructed images. Soft tissue adjacent to CM exhibited fewer artifacts and better image quality in VMI + O-MAR images than in VMI, CI + O-MAR images, and CI (P < .001). In addition, image noise and AI in VMI + O-MAR images were lower than those in VMI and CI + O-MAR images (P < .001). CT number difference was lower in VMI and VMI + O-MAR images than in CI + O-MAR images (P < .01). The CI had the highest values in image noise, AI and CT number difference (P < .001). The combination of O-MAR and 130 keV VMI showed a significant reduction of artifacts from CM than each technique alone and provided better image quality and diagnostic confidence. The combined application of O-MAR and 130 keV VMI can be a better alternative to reduce artifacts from CM in spectral-detector CT.
Keywords: artifacts; contrast media; orthopedic metal-artifact-reduction algorithm; spectral-detector CT; virtual monoenergetic images.
Copyright © 2025 the Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no funding and conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures


References
-
- Fleischmann D. Use of high-concentration contrast media in multiple-detector-row CT: principles and rationale. Eur Radiol. 2003;13(Suppl 5):M14–20. - PubMed
-
- Mitsumori LM, Wang E, May JM, et al. Triphasic contrast bolus for whole-chest ECG-gated 64-MDCT of patients with nonspecific chest pain: evaluation of arterial enhancement and streak artifact. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2010;194:W263–271. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

