Heyde syndrome: Experiences with the use of semiautomatic vWF multimer analysis for diagnosis and TAVI for treatment - case report
- PMID: 40388768
- PMCID: PMC12091634
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000042486
Heyde syndrome: Experiences with the use of semiautomatic vWF multimer analysis for diagnosis and TAVI for treatment - case report
Abstract
Rationale: Aortic stenosis (AS) is currently the most frequent valve disorder. In addition, the angiodysplasias are the most common vascular malformations of the gastrointestinal tract. Heyde syndrome (HS) is a rare disease which links these 2 pathological conditions.
Patient concerns: Currently, there are no clearly defined guidelines for the confirmation of HS diagnosis and for timing of aortic valve replacement in patients with confirmed HS, despite the fact that HS is connected with increased mortality and the need for numerous rehospitalizations and multiple blood transfusions. Therefore, the aim of this study was to report (our) first experiences with novel diagnostic method for acquired von Willebrand (vW) syndrome and transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR) for treatment of HS.
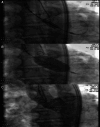
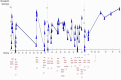
Diagnoses: We report a case of a 68-year-old man who was diagnosed with HS with the use of semiautomatic vW factor multimer analysis.
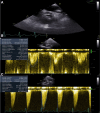
Interventions: A successful TAVR was used for treatment of AS.
Outcomes: After the interventional treatment of AS, the patient did not have a recurrence of the anemic syndrome.
Lessons: This is a unique case of a patient with HS in whom semiautomatic vW factor multimer analysis was used for diagnosis of acquired vW syndrome together with TAVR procedure for HS treatment.
Keywords: Heyde syndrome; acquired von Willebrand syndrome; aortic stenosis; semiautomatic von Willebrand factor multimer analysis.
Copyright © 2025 the Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no funding and conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures

References
-
- Warkentin TE, Moore JC, Morgan DG. Aortic stenosis and bleeding gastrointestinal angiodysplasia: is acquired von Willebrand’s disease the link? Lancet. 1992;340:35–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

