Incidental pediatric intraparenchymal meningioma: illustrative case
- PMID: 40388891
- PMCID: PMC12087368
- DOI: 10.3171/CASE24611
Incidental pediatric intraparenchymal meningioma: illustrative case
Abstract
Background: Meningiomas are the most common benign tumors among CNS neoplasms. In the pediatric population, however, they account for only 0.4%-4.6% of all intracranial neoplasms; they are rare inside the brain parenchyma and are frequently confused with other entities, such as glioneuronal tumors and cavernomas, among others.
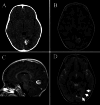
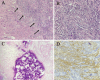
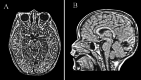
Observations: The authors describe the case of a 4-year-old male who presented to the emergency department for evaluation of periorbital cellulitis and was incidentally diagnosed with a brain tumor. MRI demonstrated an expansive heterogeneous lesion, 2.2 × 1.9 × 1.8 cm, in the left lingual gyrus. Spectroscopy and perfusion imaging suggested a low-grade glioneuronal tumor. After thorough discussion, the family and medical team elected to pursue surgical treatment. The patient had an uneventful postoperative recovery, and subsequent pathological and immunohistochemical analysis confirmed the diagnosis of a fibrous meningioma (WHO grade 1).
Lessons: Intraparenchymal meningiomas are a rare and misdiagnosed tumor, especially in the pediatric age group, and therefore are not usually considered in the differential diagnosis of intra-axial neoplasms in children. When suspected, surgery may be encouraged due to the tendency of these tumors to exhibit more aggressive behavior compared with adult meningiomas. https://thejns.org/doi/10.3171/CASE24611.
Keywords: case report; intra-axial meningioma; intraparenchymal meningioma; oncology; pediatric tumor.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Pediatric Intraparenchymal Meningioma: Case Report and Comparative Review.Pediatr Neurosurg. 2016;51(2):83-6. doi: 10.1159/000441008. Epub 2015 Nov 3. Pediatr Neurosurg. 2016. PMID: 26524676 Review.
-
Convexity dural hemangioma: illustrative case.J Neurosurg Case Lessons. 2024 Nov 18;8(21):CASE24476. doi: 10.3171/CASE24476. Print 2024 Nov 18. J Neurosurg Case Lessons. 2024. PMID: 39556829 Free PMC article.
-
A Multimodal Approach to the Treatment of Intraparenchymal Meningioma in a 7-Year-Old Boy: A Case Report.Pediatr Neurosurg. 2018;53(3):175-181. doi: 10.1159/000487808. Epub 2018 Apr 12. Pediatr Neurosurg. 2018. PMID: 29649797
-
Intraparenchymal Meningioma.J Med Cases. 2021 Jan;12(1):32-36. doi: 10.14740/jmc3592. Epub 2020 Nov 18. J Med Cases. 2021. PMID: 34434425 Free PMC article.
-
Intraparenchymal Meningioma: Clinical, Radiologic, and Histologic Review.World Neurosurg. 2016 Aug;92:23-30. doi: 10.1016/j.wneu.2016.04.098. Epub 2016 May 4. World Neurosurg. 2016. PMID: 27155381 Review.
References
-
- Liu Y Li F Zhu S Liu M Wu C.. Clinical features and treatment of meningiomas in children: report of 12 cases and literature review. Pediatr Neurosurg. 2008;44(2):112-117. - PubMed
-
- Huntoon K, Pluto CP, Ruess L.Sporadic pediatric meningiomas: a neuroradiological and neuropathological study of 15 cases. J Neurosurg Pediatr. 2017;20(2):141-148. - PubMed
-
- Rushing EJ, Olsen C, Mena H.Central nervous system meningiomas in the first two decades of life: a clinicopathological analysis of 87 patients. J Neurosurg. 2005;103(6suppl):489-495. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

