Overview of methods that determine mitochondrial function in human disease
- PMID: 40389059
- PMCID: PMC12250752
- DOI: 10.1016/j.metabol.2025.156300
Overview of methods that determine mitochondrial function in human disease
Abstract
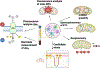
Cellular metabolism has a key role in the pathogenesis of human disease. Mitochondria are the organelles that generate most of the energy needed for a cell to function and drive cellular metabolism. Understanding the link between metabolic and mitochondrial function can be challenging due to the variation in methods used to measure mitochondrial function and heterogeneity in mitochondria, cells, tissues, and end organs. Mitochondrial dysfunction can be determined at both the cellular and tissue levels using several methods, such as assessment of cellular bioenergetics, levels of mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA), mitochondrial membrane potential (MMP), mitochondrial reactive oxygen species (mito-ROS), and levels of mitochondrial enzymes. Recent advances involving novel radiotracers in combination with PET imaging have allowed for the determination of mitochondrial function in vivo with high specificity. Understanding the barriers in existing methodologies used to study mitochondrial function may help further establish the assessment of mitochondrial function as a biologically and clinically relevant biomarker for human disease severity and prognosis. Herein, we critically review the existing literature regarding the strengths and limitations of methods that determine mitochondrial function, and we subsequently discuss how emerging research methods have begun to overcome some of these hurdles. We conclude that a combination of techniques, including respirometry and mitochondrial membrane potential assessment, is necessary to understand the complexity and biological and clinical relevance of mitochondrial function in human disease.
Keywords: Biomarkers; Human disease; Metabolism; Mitochondria; Mitrochondrial function.
Copyright © 2025 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest The authors declare the following financial interests/personal relationships which may be considered as potential competing interests: Theodoros Kelesidis reports financial support was provided by National Institutes of Health. Theodoros Kelesidis reports a relationship with National Institutes of Health that includes: funding grants. Theodoros Kelesidis is an Associate Editor for the Journal Metabolism Clinical and Experimental but was not involved in the peer review process of the manuscript. All authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The Black Book of Psychotropic Dosing and Monitoring.Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024 Jul 8;54(3):8-59. Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024. PMID: 38993656 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Signs and symptoms to determine if a patient presenting in primary care or hospital outpatient settings has COVID-19.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 20;5(5):CD013665. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013665.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35593186 Free PMC article.
-
Assessing the comparative effects of interventions in COPD: a tutorial on network meta-analysis for clinicians.Respir Res. 2024 Dec 21;25(1):438. doi: 10.1186/s12931-024-03056-x. Respir Res. 2024. PMID: 39709425 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regional cerebral blood flow single photon emission computed tomography for detection of Frontotemporal dementia in people with suspected dementia.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015 Jun 23;2015(6):CD010896. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010896.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015. PMID: 26102272 Free PMC article.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Dec 22;12(12):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Jan 9;1:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub3. PMID: 29271481 Free PMC article. Updated.
References
-
- Ravagnan L, Roumier T, Kroemer G. Mitochondria, the killer organelles and their weapons. J Cell Physiol 2002;192:131–7. - PubMed
-
- Lenaz G, Bovina C, D’Aurelio M, Fato R, Formiggini G, Genova ML, et al. Role of mitochondria in oxidative stress and aging. Ann N Y Acad Sci 2002;959:199–213. - PubMed
-
- Garcia-Ramirez M, Francisco G, Garcia-Arumi E, Hernandez C, Martinez R, Andreu AL, et al. Mitochondrial DNA oxidation and manganese superoxide dismutase activity in peripheral blood mononuclear cells from type 2 diabetic patients. Diabetes Metab 2008;34:117–24. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

