Study protocol for Active Start Active Future: a randomised control trial of an early behaviour-change intervention targeting physical activity participation and sedentary behaviour in young children with cerebral palsy living in South East Queensland, Australia
- PMID: 40389315
- PMCID: PMC12090876
- DOI: 10.1136/bmjopen-2024-087697
Study protocol for Active Start Active Future: a randomised control trial of an early behaviour-change intervention targeting physical activity participation and sedentary behaviour in young children with cerebral palsy living in South East Queensland, Australia
Abstract
Introduction: The benefits of physical activity (PA) are compelling for all ages and abilities. For children with cerebral palsy (CP), two distinct health behaviours, being physically active and reducing sedentary time, are critical to target as an early intervention to reduce long-term morbidity. One approach may be to increase PA participation by empowering parents who are key to making family lifestyle changes. This study will compare Active Start Active Future, a participation-focused intervention, to usual care in a mixed-methods randomised waitlist-controlled trial.
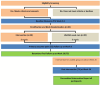
Methods and analysis: A total of 40 children with CP (3-7 years), classified in Gross Motor Function Classification System (GMFCS) levels II-V, will be stratified (GMFCS II vs III, IV vs V) and randomised to receive either (1) Active Start Active Future, an 8-week intervention for 1 hour per week in any setting or (2) usual care followed by delayed intervention. Active Start Active Future aims to increase PA and reduce sedentary behaviour of young children with CP by providing participatory opportunities to promote PA behaviour change. Outcomes will be measured at baseline (T1), immediately postintervention at 8 weeks (T2) and at 26 weeks postbaseline (T3). The primary outcomes are the Canadian Occupational Performance Measure for both child and parent participation goals and child physical performance goal. Secondary outcomes include daily time spent in moderate to vigorous PA and sedentary time, gross motor function, quality of life, barriers to participation for the children and parents' PA and sedentary time. Intervention acceptability and experiences of PA participation will be explored using a qualitative descriptive approach.
Ethics and dissemination: The Children's Health Queensland Hospital and Health Service Human Research Ethics Committee (HREC/23/QCHQ/100850) and The University of Queensland Human Research Ethics Committee (2024/HE000054) have approved this study. The results of the study will be disseminated to families and community agencies as guided by our advisory group and as conference abstracts and presentations, peer-reviewed articles in scientific journals and institution newsletters and media releases.
Trial registration number: ACTRN12624000042549, Universal Trial Number: U1111-1300-7421; Australian New Zealand Clinical Trials Registry.
Keywords: Child; Family; Patient Participation; REHABILITATION MEDICINE; Randomized Controlled Trial.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2025. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ Group.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures
Similar articles
-
ACTIVE STRIDES-CP: protocol for a randomised trial of intensive rehabilitation (combined intensive gait and cycling training) for children with moderate-to-severe bilateral cerebral palsy.BMJ Open. 2023 Mar 29;13(3):e068774. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2022-068774. BMJ Open. 2023. PMID: 36990490 Free PMC article.
-
Participate CP 2: optimising participation in physically active leisure for children with cerebral palsy - protocol for a phase III randomised controlled trial.BMJ Open. 2023 Oct 3;13(10):e075570. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2023-075570. BMJ Open. 2023. PMID: 37788925 Free PMC article.
-
ParticiPAte CP: a protocol of a randomised waitlist controlled trial of a motivational and behaviour change therapy intervention to increase physical activity through meaningful participation in children with cerebral palsy.BMJ Open. 2017 Aug 7;7(8):e015918. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2017-015918. BMJ Open. 2017. PMID: 28790038 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Mechanically assisted walking training for walking, participation, and quality of life in children with cerebral palsy.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Nov 18;11(11):CD013114. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013114.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. PMID: 33202482 Free PMC article.
-
Folic acid supplementation and malaria susceptibility and severity among people taking antifolate antimalarial drugs in endemic areas.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Feb 1;2(2022):CD014217. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD014217. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 36321557 Free PMC article.
References
-
- World Health Organisation . WHO guidelines on physical activity and sedentary behaviour. Geneva: World Health Organisation; 2020. - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization . International classification of functioning, disability, and health: ICF. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2001.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous