Effect of Baduanjin on postoperative activity tolerance, lung function and negative emotions in patients with lung cancer: a protocol for systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 40389318
- PMCID: PMC12090857
- DOI: 10.1136/bmjopen-2024-093152
Effect of Baduanjin on postoperative activity tolerance, lung function and negative emotions in patients with lung cancer: a protocol for systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Introduction: Patients who have undergone lung cancer surgery often experience reduced exercise tolerance, impaired lung function and increased negative emotions such as anxiety and depression. Baduanjin, a traditional Chinese mind-body exercise, has shown benefits in improving exercise tolerance and lung function in populations with chronic diseases. However, evidence on the effectiveness of Baduanjin for post-lung cancer surgery patients remains limited. This study aims to systematically assess the impact of Baduanjin on exercise tolerance, lung function and emotional well-being in these patients.
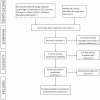
Methods and analysis: We will conduct a comprehensive search of PubMed, the Cochrane Library, China National Knowledge Infrastructure, Chinese Biomedical Literatures database, Wangfang database and China Science and Technology Journal Database (VIP) to identify randomised controlled trials (RCTs) assessing Baduanjin in postoperative lung cancer patients. The primary outcome measure will be the 6-minute walk test distance. We will assess the risk of bias in included RCTs using the bias risk assessment form from the Cochrane Collaboration Handbook. This protocol follows the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-analyses Protocols 2015 guidelines.
Ethics and dissemination: Ethical approval is not required as no primary data are collected. The results will be presented at scientific conferences or submitted to a peer-reviewed scientific journal.
Prospero registration number: CRD42024570196.
Keywords: COMPLEMENTARY MEDICINE; Lung Diseases; ONCOLOGY; Rehabilitation medicine; SPORTS MEDICINE.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2025. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ Group.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effectiveness of Traditional Chinese Medicine in Psychological Rehabilitation After Lung Cancer Surgery: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis protocol.Integr Cancer Ther. 2025 Jan-Dec;24:15347354251313533. doi: 10.1177/15347354251313533. Integr Cancer Ther. 2025. PMID: 39799478 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Baduanjin on postoperative rehabilitation of patients with breast cancer: A protocol for systematic review and meta-analysis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2021 Apr 30;100(17):e25670. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000025670. Medicine (Baltimore). 2021. PMID: 33907134 Free PMC article.
-
Cardiac rehabilitation of Baduanjin exercise in coronary heart disease after PCI: A protocol for systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.Medicine (Baltimore). 2021 Apr 16;100(15):e25501. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000025501. Medicine (Baltimore). 2021. PMID: 33847664 Free PMC article.
-
Folic acid supplementation and malaria susceptibility and severity among people taking antifolate antimalarial drugs in endemic areas.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Feb 1;2(2022):CD014217. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD014217. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 36321557 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Baduanjin exercise on motor function, balance and gait in Parkinson's disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis.BMJ Open. 2022 Nov 15;12(11):e067280. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2022-067280. BMJ Open. 2022. PMID: 36379643 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical