The diagnostic value of two-dimensional shear-wave elastography in identifying malignant lesions in lymph nodes: a prospective study
- PMID: 40389433
- PMCID: PMC12089400
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-00502-8
The diagnostic value of two-dimensional shear-wave elastography in identifying malignant lesions in lymph nodes: a prospective study
Abstract
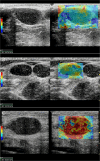
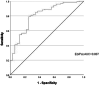
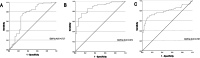
This study evaluates the diagnostic performance of two-dimensional shear wave elastography (2D-SWE) in differentiating between benign, metastatic lymph nodes (LNs) and lymphomas. From May 2022 to February 2023, a total of 137 patients who presented with unexplained LN enlargement were examined at the Ultrasound Medical Department of Union Hospital of Huazhong University of Science and Technology. The conventional ultrasound recorded the location, longitudinal diameter, transverse diameter, L/T ratio, blood supply mode, lymphatic hilum and 2D-SWE calculated the average elasticity (E) of LN. Histopathology was the diagnostic gold standard. A total of 124 patients with 159 superficial LNs were included (32 benign, 70 metastatic, 57 lymphoma). Malignant LNs had significantly higher E values than benign ones (49.38 ± 29.96 kPa vs. 25.00 ± 14.42 kPa, P < 0.001). When E > 25.46 kPa, the AUC, sensitivity, specificity, PPV, NPV and accuracy were 0.807, 0.787, 0.750, 0.926, 0.471 and 0.780, respectively, in identifying malignant LNs. For distinguishing benign LNs from lymphoma, the E cutoff was 25.03 kPa, with the AUC, sensitivity, specificity, PPV, NPV and accuracy of 0.727, 0.754, 0.719, 0.827, 0.622 and 0.742, respectively. To differentiate benign from metastatic LNs, an E cutoff of 36.97 kPa yielded an AUC, sensitivity, specificity, PPV, NPV and accuracy of 0.872, 0.757, 0.875, 0.930, 0.622 and 0.794, respectively. Comparing lymphoma and metastatic LNs, the E cutoff was 42.57 kPa. And the AUC, sensitivity, specificity, PPV, NPV and accuracy were 0.787, 0.700, 0.860, 0.860, 0.700 and 0.772, respectively. 2D-SWE parameter (the average elasticity) can effectively evaluate benign, metastatic LNs and lymphoma, which provides valuable information for preoperative evaluation of superficial LNs.
Keywords: Differential diagnosis; Shear-wave elastography; Superficial lymph nodes; Ultrasound.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interest: The authors declare no competing interests. Ethics approval and consent to participate: The study was approved by the Ethics Committee of Union Hospital affiliated to Tongji Medical College of Huazhong University of Science and Technology, and obtained the informed consent of all patients. (Ethics approval ID: UHCT-IEC-SOP-016-03-01)
Figures
Similar articles
-
Differential Diagnosis Value of Shear-Wave Elastography for Superficial Enlarged Lymph Nodes.Front Oncol. 2022 Jun 30;12:908085. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.908085. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35847906 Free PMC article.
-
Quantitative and Qualitative Approach for Shear Wave Elastography in Superficial Lymph Nodes.Ultrasound Med Biol. 2021 Aug;47(8):2117-2127. doi: 10.1016/j.ultrasmedbio.2021.04.008. Epub 2021 May 28. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2021. PMID: 34059376
-
2D-shear wave elastography in the evaluation of suspicious superficial inguinal lymph nodes: Reproducibility and region of interest selection.PLoS One. 2022 Mar 28;17(3):e0265802. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0265802. eCollection 2022. PLoS One. 2022. PMID: 35344561 Free PMC article.
-
Transcutaneous Ultrasound: Elastographic Lymph Node Evaluation. Current Clinical Applications and Literature Review.Ultrasound Med Biol. 2016 Jan;42(1):16-30. doi: 10.1016/j.ultrasmedbio.2015.09.005. Epub 2015 Oct 17. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2016. PMID: 26489365 Review.
-
Differentiating benign from malignant superficial lymph nodes with sonoelastography.Med Ultrason. 2013 Jun;15(2):132-9. doi: 10.11152/mu.2013.2066.152.smd1cbj2. Med Ultrason. 2013. PMID: 23702503 Review.
References
-
- Zhang, X., Liu, Y., Luo, H. & Zhang, J. PET/CT and MRI for identifying axillary lymph node metastases in breast Cancer patients: systematic review and Meta-Analysis. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging. 52, 1840–1851 (2020). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

