Gender differences in global antimicrobial resistance
- PMID: 40389466
- PMCID: PMC12089330
- DOI: 10.1038/s41522-025-00715-9
Gender differences in global antimicrobial resistance
Abstract
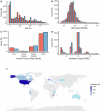
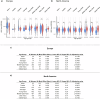
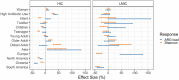
Antimicrobial resistance is one of the leading causes of mortality globally. However, little is known about the distribution of antibiotic resistance genes (ARGs) in human gut metagenomes, collectively referred to as the resistome, across socio-demographic gradients. In particular, limited evidence exists on gender-based differences. We investigated how the resistomes differ between women and men in a global dataset of 14,641 publicly available human gut metagenomes encompassing countries with widely variable economic statuses. We observed a 9% higher total ARG load in women than in men in high-income countries. However, in low- and middle-income countries, the difference between genders was reversed in univariate models, but not significant after adjusting for covariates. Interestingly, the differences in ARG load between genders emerged in adulthood, suggesting resistomes differentiate between genders after childhood. Collectively, our data-driven analyses shed light on global, gendered antibiotic resistance patterns, which may help guide further research and targeted interventions.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Joos, R. et al. Examining the healthy human microbiome concept. Nat. Rev. Microbiol.23, 192–205 (2025). - PubMed
-
- Organization, W. H. Tackling antimicrobial resistance (AMR) together: working paper 5.0: enhancing the focus on gender and equity. (2018).
-
- Collignon, P., Beggs, J. J., Walsh, T. R., Gandra, S. & Laxminarayan, R. Anthropological and socioeconomic factors contributing to global antimicrobial resistance: a univariate and multivariable analysis. Lancet Planet Health2, e398–e405 (2018). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 952914/European Union's Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme
- 952914/European Union's Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme
- 952914/European Union's Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme
- 952914/European Union's Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme
- 330887/Research Council of Finland,Finland
- 330887/Research Council of Finland,Finland
- 348439/Research Council of Finland,Finland
- 330887/Research Council of Finland,Finland
- 20220114/Alhopuro Foundation
- 20220114/Alhopuro Foundation
- 2019-00299/Swedish Research Council
- FFL21-0174/Swedish Foundation for Strategic Research
- KAW 2020.0239/Data-Driven Life Science
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

