Second-derivative UV spectral analysis of aqueous humor for eye disease diagnosis and assessing the effects of food additives on ocular health
- PMID: 40389612
- PMCID: PMC12089584
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-02190-w
Second-derivative UV spectral analysis of aqueous humor for eye disease diagnosis and assessing the effects of food additives on ocular health
Abstract
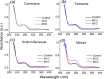
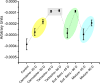
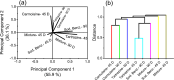
Ultraviolet absorption (UV) spectroscopy is an invaluable method for analyzing compounds in ocular fluids, identifying chemical structures, and understanding molecular interactions. The widespread use of additives in food production is well documented; these additives color, flavor, preserve, and enhance the texture or nutrition of food, ensuring a broader range of products and reducing costs. This study employed UV spectroscopy to examine changes in aqueous humor composition after daily intake of permitted amounts of food additives over 45-90 days. The rats were administered colorant dyes (carmoisine or tartrazine), a sodium benzoate preservative, or a combination of all three through oral gavage. Aqueous humor samples were collected post sedation from the anterior chamber via a 30-gauge needle without additional processing. The spectra of these samples were analyzed via secondary derivative calculations and chemometric analysis (principal component and hierarchical analyses) with OriginPro 2015 software. The common outcome observed was ocular toxicity, resulting from decreased antioxidant defense mechanisms, leading to ocular side effects on the cornea and lens. These changes in aqueous humor composition are indirectly linked to food additives rather than the mechanisms of aqueous humor formation.
Keywords: Aqueous humor; Chemometric analysis; Eye; Second derivative; UV spectroscopy.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests. Ethical approval and consent to participate: The handling of the animals followed the guidelines set forth by the Association for Research in Vision and Ophthalmology (ARVO) regarding the use of animals in ophthalmic research. Additionally, the research protocol received approval from the local ethical committee.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The effect of aqueous humor ascorbate on ultraviolet-B-induced DNA damage in lens epithelium.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1998 Feb;39(2):344-50. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1998. PMID: 9477992
-
Effect of UV-A and UV-B irradiation on the metabolic profile of aqueous humor in rabbits analyzed by 1H NMR spectroscopy.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2005 Mar;46(3):776-81. doi: 10.1167/iovs.04-0787. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2005. PMID: 15728530
-
Water soluble antioxidants in mammalian aqueous humor: interaction with UV B and hydrogen peroxide.Vision Res. 1998 Oct;38(19):2881-8. doi: 10.1016/s0042-6989(98)00069-8. Vision Res. 1998. PMID: 9797984
-
Analysis of pharmaceuticals and small molecules in aqueous humor.J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2018 Sep 10;159:23-36. doi: 10.1016/j.jpba.2018.06.049. Epub 2018 Jun 25. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2018. PMID: 29980016 Review.
-
Novel roles for the lens in preserving overall ocular health.Exp Eye Res. 2017 Mar;156:117-123. doi: 10.1016/j.exer.2016.05.027. Epub 2016 Jun 6. Exp Eye Res. 2017. PMID: 27282996 Review.
References
-
- Toris, C. B., Tye, G. & Pattabiraman, P. Changes in parameters of aqueous humor dynamics throughout life. 161–190. 10.1007/978-3-030-25886-3_6 (2019).
-
- Toris, C. B., Oostra, T. D. & Martinez, C. E. Aqueous humor, glaucoma, and corneal health. in The Science of Glaucoma Management 217–229 (Elsevier, 2023). 10.1016/B978-0-323-88442-6.00017-0
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

