Major ion chemistry and suitability of groundwater resources for different utilizations in mica mining areas, Jharkhand, India
- PMID: 40389614
- PMCID: PMC12090656
- DOI: 10.1186/s12932-025-00099-x
Major ion chemistry and suitability of groundwater resources for different utilizations in mica mining areas, Jharkhand, India
Abstract
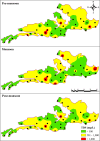
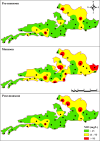
Groundwater resources in mica mining areas of Jharkhand are vital for local communities, agriculture, and domestic utilization. The study investigates the major ion chemistry of groundwater in the mica mining regions, focusing on key physicochemical parameters such as pH, electrical conductivity (EC), total dissolved solids (TDS), and concentrations of major cations (Ca²⁺, Mg²⁺, Na⁺, K⁺) and anions (HCO₃⁻, Cl⁻, SO₄²⁻, NO₃⁻, F-). Groundwater samples from the study area were collected before the monsoon season, during the monsoon season, and after the monsoon season. The hydro-chemical analysis reveals that groundwater in the mica mining zones exhibits elevated levels of dissolved ions, with NO₃⁻, F-, Ca²⁺, Mg²⁺ and total hardness exceeding permissible limits set by Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS) for drinking purposes at some locations. Water Quality Index (WQI) assessments suggest that a significant proportion of groundwater samples fall into the "good" to "very good" category for drinking and about 29% of the samples fall under the "poor" category. The groundwater was generally suitable for irrigational use with exception of a few due to high salinity. The principal component analysis revealed rock weathering as a dominant source of ions along with anthropogenic sources like mining and agriculture contributing minorly to the ionic load. The predominant hydro-chemical facies identified were Ca-Mg-HCO3 and Ca-Mg-Cl-SO4 types. Both carbonate and silicate weathering play an important role in the geochemical signature of the groundwater in the area. The study implicates the potential health impacts of using the groundwater as drinking water without treatment at a few locations owing to high fluoride, nitrate and dissolved solids. The study also highlights the need for sustainable water management practices and regular monitoring of groundwater quality to mitigate the anthropogenic impacts on groundwater resources.
Keywords: Drinking water suitability; Groundwater quality; Irrigational suitability; Mica mining; Principal component analysis; Water quality index.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: Two of the co-authors (Dr. Abhay Kumar Singh and Dr. Ashwani Kumar Tiwari) are the guest editors of the special issue to which the manuscript is being submitted.
Figures










Similar articles
-
Groundwater Geochemistry, Sources Identification and Quality Assessment in Umaria Coalfield, Madhya Pradesh, India.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2025 May;32(25):15436-15454. doi: 10.1007/s11356-025-36595-x. Epub 2025 Jun 11. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2025. PMID: 40500526
-
Deciphering geochemical fingerprints and health implications of groundwater fluoride contamination in mica mining regions using machine learning tactics.Environ Geochem Health. 2024 Aug 27;46(10):400. doi: 10.1007/s10653-024-02177-y. Environ Geochem Health. 2024. PMID: 39190109
-
Geochemical characterisation and geostatistical evaluation of groundwater suitability: a case study in Perambalur District, Tamil Nadu, India.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2023 May;30(22):62653-62674. doi: 10.1007/s11356-023-26387-6. Epub 2023 Mar 22. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2023. PMID: 36947380
-
Evaluation of water quality index and geochemical characteristics of surfacewater from Tawang India.Sci Rep. 2022 Jul 9;12(1):11698. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-14760-3. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35810170 Free PMC article.
-
Sustainable groundwater management through water quality index and geochemical insights in Valsad India.Sci Rep. 2025 Mar 13;15(1):8769. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-92053-1. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40082503 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Scanlon BR, Fakhreddine S, Rateb A, De Graaf I, Famiglietti J, Gleeson T, Zheng C (2023) Global water resources and the role of groundwater in a resilient water future. Nat Rev Earth Environ 4(2):87–101
-
- Saha D, Ray RK (2019) Groundwater resources of India: potential, challenges and management. Groundwater development and management: issues and challenges in South Asia, 19–42
-
- Akhtar N, Syakir Ishak MI, Bhawani SA, Umar K (2021) Various natural and anthropogenic factors responsible for water quality degradation: A review. Water 13(19):2660
-
- Madhav S, Ahamad A, Singh AK, Kushawaha J, Chauhan JS, Sharma S, Singh P (2020) Water pollutants: sources and impact on the environment and human health. Sens Water Pollutants Monitoring: Role Mater, 43–62
-
- Balderacchi M, Benoit P, Cambier P, Eklo OM, Gargini A, Gemitzi A, Trevisan M (2013) Groundwater pollution and quality monitoring approaches at the European level. Crit Rev Environ Sci Technol 43(4):323–408
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

