Somatic PIK3R1 mutations in the iSH2 domain are accessible to PI3Kα inhibition
- PMID: 40389643
- PMCID: PMC12254339
- DOI: 10.1038/s44321-025-00249-9
Somatic PIK3R1 mutations in the iSH2 domain are accessible to PI3Kα inhibition
Abstract
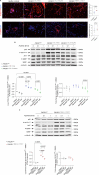
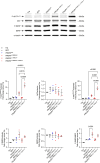
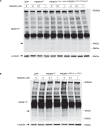
Mutations in PIK3R1 have recently been identified in patients with overgrowth syndromes and complex vascular malformations. PIK3R1 encodes p85α which acts as the regulatory subunit of the lipid kinase PI3Kα. PIK3R1 mutations result in the excessive activation of the AKT/mTOR pathway. Currently, there are no approved treatments specifically dedicated to patients with PIK3R1 mutations, and medical care primarily focuses on managing symptoms. In this study, we identified three patients, including two children, who had mosaic somatic PIK3R1 mutations affecting the iSH2 domain, along with severe associated symptoms that were unsuccessfully treated with rapamycin. We conducted in vitro experiments to investigate the impact of these mutations, including a double PIK3R1 mutation in cis observed in one patient. Our findings revealed that p85α mutants in the iSH2 domain showed sensitivity to alpelisib, a pharmacological inhibitor of PI3Kα. Based on these findings, we received authorization to administer alpelisib to all three patients. Following drug introduction, patients rapidly demonstrated clinical improvement, pain, fatigue and inflammatory flares were attenuated. Magnetic Resonance Imaging showed a mean decrease of 22.67% in the volume of vascular malformations over twelve months of treatment with alpelisib. No drug-related adverse events were reported during the course of the study. In conclusion, this study provides support for the use of PI3Kα inhibition as a promising therapeutic approach for individuals with PIK3R1-related anomalies.
Keywords: Alpelisib; Overgrowth Syndrome; PIK3R1-Related Disorders; Vascular Malformations; p85.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure and competing interests statement. A patent application (“BYL719 (alpelisib) for use in the treatment of PIK3CA-related overgrowth spectrum” #WO2017140828A1) has been filed by INSERM (Institut National de la Santé et de la Recherche Médicale), Centre National De La Recherche Scientifique (CNRS), Université Paris Cité, and Assistance Publique-Hôpitaux De Paris (AP-HP) for the use of BYL719 (alpelisib) in the treatment of PIK3CA-related overgrowth spectrum (PROS/CLOVES syndrome). G. Canaud is the inventor. This patent is licensed to Novartis. Guillaume Canaud receives or has received consulting fees from Novartis, Fresenius Medical Care, Vaderis, Alkermes, IPSEN and BridgeBio. The other authors declare no other competing interests. Guillaume Canaud is an editorial advisory board member. This has no bearing on the editorial consideration of this article for publication.
Figures





References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 101000948/EC | ERC | HORIZON EUROPE European Research Council (ERC)
- ANR-18-RHUS-005/Agence Nationale de la Recherche (ANR)
- 19-CE14-0030-01/Agence Nationale de la Recherche (ANR)
- 2023/Fondation d'entreprise IRCEM
- 2021/Fonds de dotation Emmanuel BOUSSARD
- 2023 Signalopathies/MSD Avenir
- 2020/Fondation DAY SOLVAY
- 2019/the Fondation Line RENAUD-Loulou GASTE
- 2019/Fondation Schlumberger pour l'Education et la Recherche (FSER)
- 2019/Fondation Maladies Rares (FMR)
- 2021/Association Robert Debré pour la Recherche Médicale
- FDM202006011222/Fondation pour la Recherche Médicale (FRM)
- 472149/Banting Postdoctoral Fellowship
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

