A pharmaco-metabolomics study of Glycyrrhiza glabra, Boswellia sarca, and Acacia nilotica in acute allergic dermatitis
- PMID: 40389681
- PMCID: PMC12176975
- DOI: 10.1007/s10787-025-01761-7
A pharmaco-metabolomics study of Glycyrrhiza glabra, Boswellia sarca, and Acacia nilotica in acute allergic dermatitis
Abstract
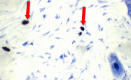
Acute allergic contact dermatitis is an inflammatory skin condition characterized by swollen, itchy lesions. This study aimed to evaluate the soothing and wound-healing effects of fixed and volatile oils of Boswellia sarca, as well as extracts of Glycyrrhiza glabra and Acacia nilotica, on acute contact dermatitis in rats. Phytochemical analysis revealed the presence of flavonoids, tannins, saponins, triterpenoids, alkaloids, and cardiac glycosides in Acacia nilotica and, Glycyrrhiza glabra extracts, with Boswellia sarca showing a dominance of volatile oils. The study included a normal group and six acute allergic dermatitis groups induced by subcutaneous histamine injection. One group served as a positive control without treatment, while five groups were treated topically at inflamed sites with Boswellia sarca oils, Glycyrrhiza glabra, and Acacia nilotica extracts, alongside betamethasone as a standard treatment. The effects were evaluated through inspection, serum levels of ICAM-1, LTB4, and ILβ-4, as well as histopathological and immunohistochemical analyses. GC/MS analysis identified Incensole acetate (50.12%) and Incensole (32.44%) as major compounds in BS fixed oil, with significant terpenoids and volatile components. Metabolomic profiling using LC-MS/MS highlighted diverse secondary metabolites in Acacia nilotica and, Glycyrrhiza glabra, including polyphenolic acids, flavonoids, and amino acids, showcasing their therapeutic potential. All topical treatments reduced ICAM-1 and LTB4 levels to varying degrees and exhibited better histopathological and immunohistochemical results compared to the untreated positive control group. Among the treatments, Boswellia oils and, Glycyrrhiza glabra extracts demonstrated the most effective soothing and curative effects on allergic dermatitis. Boswellia sarca oils and, Glycyrrhiza glabra extract showed the best soothing and curative effects against allergic dermatitis.
Keywords: Acacia nilotica; Boswellia sarca; Glycyrrhiza glabra; Acute dermatitis; Histamine.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing Interests: The authors declare that there is no competing interest of any type regarding the current research article.
Figures


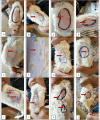

 Significant difference from Betamethasone group, #Significant difference from Volatile oil of Frakisence group,&Significant difference from Fixed oil of Frakisence group
Significant difference from Betamethasone group, #Significant difference from Volatile oil of Frakisence group,&Significant difference from Fixed oil of Frakisence group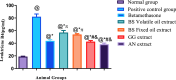
 Significant difference from Betamethasone group, #Significant difference from Volatile oil of Frakisence group,&Significant difference from Fixed oil of Frakisence group
Significant difference from Betamethasone group, #Significant difference from Volatile oil of Frakisence group,&Significant difference from Fixed oil of Frakisence group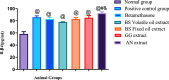
 4 + SE, N = 5, ANOVA test was used to compare means, followed by the Tukey–Kramer multiple comparisons test. P ≤ 0.05. @Significant difference from negative control group,#Significant difference from Volatile oil of Frakisence group,&Significant difference from Fixed oil of Frakisence group
4 + SE, N = 5, ANOVA test was used to compare means, followed by the Tukey–Kramer multiple comparisons test. P ≤ 0.05. @Significant difference from negative control group,#Significant difference from Volatile oil of Frakisence group,&Significant difference from Fixed oil of Frakisence group
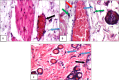





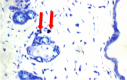
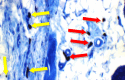
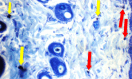
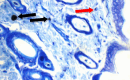


References
-
- Abeles AM, Pillinger MH, Abramson SB (2015) Inflammation and its mediators Rheumatology. Elsevier, Netherlands p 169–182
-
- Aboul Naser AF, Ahmed YR, Mohammed MA et al (2024) Inflammatory mediators, oxidative stress and genetic disturbance in rheumatoid arthritis rats supported by alfalfa seeds metabolomic constituents via blocking interleukin-1receptor. Chem Biodivers 21(2):e202301653 - PubMed
-
- Aiello RJ, Bourassa P-A, Lindsey S, Weng W, Freeman A, Showell HJ (2002) Leukotriene B4 receptor antagonism reduces monocytic foam cells in mice. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 22(3):443–449 - PubMed
-
- Ali M, Muazu L, Nas FS, Ibrahim YS (2024) Dermatitis; types, causes. Symptoms Manag: A Rev Dermis 4(2):1–4
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
