Exploring α-Syn's Functions Through Ablation Models: Physiological and Pathological Implications
- PMID: 40389720
- PMCID: PMC12089638
- DOI: 10.1007/s10571-025-01560-2
Exploring α-Syn's Functions Through Ablation Models: Physiological and Pathological Implications
Abstract
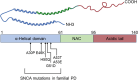
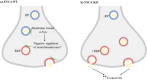
A significant advancement in neurodegenerative research was the discovery that α-synuclein (α-Syn/SNCA) plays a part in the pathophysiology of Parkinson's disease (PD). Decades later, the protein's significant impacts on various brain disorders are still being extensively explored. In disease conditions, α-Syn misfolds and forms abnormal aggregates that accumulate in neurons, thus triggering various organellar dysfunctions and ultimately neurodegeneration. These misfolded forms are highly heterogeneous and vary significantly among different synucleinopathies, such as PD, Multiple System Atrophy, or Dementia with Lewy bodies. Though initially believed to be exclusively localized in the brain, numerous pieces of evidence suggest that α-Syn functions transcend the central nervous system, with roles in peripheral functions, such as modulation of immune responses, hematopoiesis, and gastrointestinal regulation. Here, we aim to provide a detailed compilation of cellular functions and pathological phenotypes that are altered upon attenuation of α-Syn function in vitro and in vivo and explore the effects of SNCA gene silencing in healthy and disease states using cellular and animal models.
Keywords: SNCA; α-Syn; Ablation models; Parkinson's disease; Synuclein.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Conflict of interest: The authors declare no competing interests. Ethical Approval: Not applicable. Consent to Participate: Not applicable. Consent to Publish: Not applicable.
Figures


References
-
- Abeliovich A, Schmitz Y, Fariñas I, Choi-Lundberg DL, Ho WH, Castillo PE, Shinsky N, Manuel J, Verdugo JM, Armanini M, Ryan A, Hynes M, Phillips H (2000) Mice lacking α-synuclein display functional deficits in the nigrostriatal dopamine system. Neuron 25(1):239–252. 10.1016/S0896-6273(00)80886-7 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

