Characteristic analysis of N6-methyladenine in different parts of yak epididymis
- PMID: 40389816
- PMCID: PMC12087211
- DOI: 10.1186/s12864-025-11684-w
Characteristic analysis of N6-methyladenine in different parts of yak epididymis
Abstract
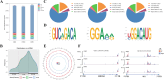
Background: The epididymis is essential for sperm maturation. During sperm maturation, markable alterations of the payload of small noncoding RNAs are observed in the epididymis, which indicated the role of epigenetic alterations in sperm maturation. However, the N6-Methyladenosine (m6A) modification profile of the epididymis remains unelucidated. Therefore, in this study, we assessed the m6A modification levels in the caput, corpus, and cauda of the yak epididymis using a combination of methylated RNA immunoprecipitation and RNA sequencing.
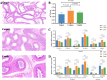
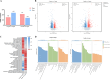
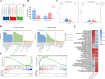
Results: The m6A levels were significantly increased in the corpus of the epididymis. Functional enrichment analysis of differentially methylated RNA (DMR) between the corpus and caput group revealed the significant enrichment of DMRs in the gap junction, ErbB signaling pathway, and mTOR signaling pathway, which participate in cell communication and sperm maturation. In addition, the DMRs of cauda-vs-corpus group were enriched in apoptosis, the FoxO signaling pathway, the PI3K-Akt signaling pathway, and the tumor necrosis factor signaling pathway that were associated with sperm autophagy, oxidative stress, and sperm maturation. Furthermore, we identified the key genes exhibiting significant changes in m6A levels but with no differences in RNA levels, including YY1-associated factor 2, forkhead box J2, and forkhead box O1. This finding indicated that m6A modifications affect these genes during translation, thereby participating in sperm maturation.
Conclusions: In summary, we generated the m6A profile of the yak epididymis, which will aid in further elucidating the maturation process of sperm and reveal more information related to male infertility.
Keywords: N 6-Methyladenosine; Epididymis; Reproductive physiology; Sperm maturation; Yak.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: The study was conducted according to the Declaration of Helsinki guidelines and was approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee of the Lanzhou Institute of Husbandry and Pharmaceutical Sciences of the Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences (LIHPS-2022-0144). Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The expression spectrum of yak epididymal epithelial cells reveals the functional diversity of caput, corpus and cauda regions.Genomics. 2024 Sep;116(5):110912. doi: 10.1016/j.ygeno.2024.110912. Epub 2024 Aug 6. Genomics. 2024. PMID: 39117249 Review.
-
Region-specific gene expression in the epididymis of Yak.Theriogenology. 2019 Nov;139:132-146. doi: 10.1016/j.theriogenology.2019.08.006. Epub 2019 Aug 5. Theriogenology. 2019. PMID: 31404823
-
CpG DNA methylation changes during epididymal sperm maturation in bulls.Epigenetics Chromatin. 2023 May 30;16(1):20. doi: 10.1186/s13072-023-00495-6. Epigenetics Chromatin. 2023. PMID: 37254160 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative rna-seq analysis of region-specific miRNA expression in the epididymis of cattleyak.Reprod Domest Anim. 2021 Apr;56(4):555-576. doi: 10.1111/rda.13893. Epub 2021 Feb 14. Reprod Domest Anim. 2021. PMID: 33438262
-
The current perspective on genetic and epigenetic factors in sperm maturation in the epididymis.Andrologia. 2021 Apr;53(3):e13989. doi: 10.1111/and.13989. Epub 2021 Jan 25. Andrologia. 2021. PMID: 33491190 Review.
References
-
- Liu N, Pan T. N6-methyladenosine–encoded epitranscriptomics. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2016;23:98–102. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

