The impact of GBSSI inactivation on starch structure and functionality in EMS-induced mutant lines of wheat
- PMID: 40389819
- PMCID: PMC12087110
- DOI: 10.1186/s12864-025-11630-w
The impact of GBSSI inactivation on starch structure and functionality in EMS-induced mutant lines of wheat
Abstract
Background: Starch, a major component of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) grain, plays a crucial role in determining processing quality. Granule-bound starch synthase I (GBSSI), the enzyme primarily responsible for elongating α-1,4-glucan chains into linear amylose molecules, is a key determinant of starch quality. In this study, a mutant population of the wheat cultivar SM126, a high-quality variety form Sichuan, China, was generated using ethyl methanesulfonate (EMS) mutagenesis. This research investigates the effects of GBSSI inactivation on starch structure and functionality.
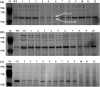
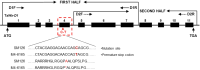
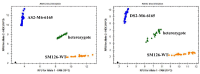
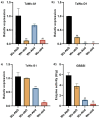
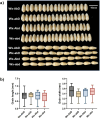
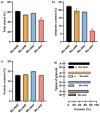
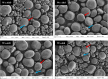
Results: A waxy mutant (Wx-Abd) was identified by screening an M4 seed library with sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE) of grain endosperm flour. DNA sequencing revealed a single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) in the fourth exon, causing a premature stop codon and inactivation of the Wx-Abd allele. In previous work, the Wx-abD mutant was identified in the M2 generation, and crossing the M2-31 line with the M4-6165 line produced four distinct Wx protein subunits in the SM126 background. Comparisons between the Wx-abd line and the wild-type SM126 (Wx-AbD) showed significant differences in starch properties. The Wx-abd line exhibited reduced Wx gene expression, a distinct surface depression on starch granules, and a higher proportion of B-type starch granules. Notably, it exhibited significantly lower amylose content (7.02%) compared to SM126 (22.32%), along with a reduction in total starch content. Additionally, the Wx-abd line showed a higher gelatinization temperature.
Conclusion: Inactivation of GBSSI in the Wx-abd line resulted in altered starch structure, particularly a decrease in amylose content and changes in granule morphology. These findings suggest that the Wx-abd line represents a valuable genetic resource for wheat breeding programs focused on improving starch quality for food production, with its high agronomic performance making it suitable for further breeding applications.
Keywords: GBSSI; Gene expression; Starch properties; Thermodynamic properties; Waxy wheat.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: The authors declare that all studies comply with relevant institutional, national, and international guidelines and legislation for plant ethics in the methods section. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Reducing amylose content in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) using a novel Wx-D1 null allele generated by chemical mutagenesis.J Sci Food Agric. 2025 Mar 15;105(4):2332-2341. doi: 10.1002/jsfa.14003. Epub 2024 Nov 6. J Sci Food Agric. 2025. PMID: 39503064
-
A single base change at exon of Wx-A1 caused gene inactivation and starch properties modified in a wheat EMS mutant line.J Sci Food Agric. 2022 Mar 30;102(5):2012-2022. doi: 10.1002/jsfa.11540. Epub 2021 Oct 7. J Sci Food Agric. 2022. PMID: 34558070
-
Identification and molecular characterization of mutant line deficiency in three waxy proteins of common wheat (Triticum aestivum L.).Sci Rep. 2021 Feb 10;11(1):3510. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-82865-2. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 33568721 Free PMC article.
-
Wheat waxy proteins: polymorphism, molecular characterization and effects on starch properties.Theor Appl Genet. 2016 Jan;129(1):1-16. doi: 10.1007/s00122-015-2595-9. Epub 2015 Aug 15. Theor Appl Genet. 2016. PMID: 26276148 Review.
-
Posttranslational Modification of Waxy to Genetically Improve Starch Quality in Rice Grain.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 May 3;22(9):4845. doi: 10.3390/ijms22094845. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34063649 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Lan J, Li Y, Xu K, Zhang X, Tang H, Qi P, Ma J, Wang J, Chen G, Pu Z. EMS induced SNP changes led to mutation of Wx protein in common wheat. Cereal Res Commun. 2020;48:233–8.
-
- Park IM, Ibáñez AM, Shoemaker CF. Rice starch molecular size and its relationship with amylose content. Starch-Stärke. 2007;59(2):69–77.
-
- Jeon J-S, Ryoo N, Hahn T-R, Walia H, Nakamura Y. Starch biosynthesis in cereal endosperm. Plant Physiol Biochem. 2010;48(6):383–92. - PubMed
-
- Manners DJ. Recent developments in our Understanding of amylopectin structure. Carbohydr Polym. 1989;11(2):87–112.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

