Gemcitabine resistance by CITED4 upregulation via the regulation of BIRC2 expression in pancreatic cancer
- PMID: 40389954
- PMCID: PMC12090687
- DOI: 10.1186/s12929-025-01140-y
Gemcitabine resistance by CITED4 upregulation via the regulation of BIRC2 expression in pancreatic cancer
Abstract
Background: Gemcitabine (GEM) is used as a first-line therapy for patients diagnosed with any stage of pancreatic cancer (PC); however, patient survival is poor because of GEM resistance. Thus, new approaches to overcome GEM resistance in PC are urgently needed. Here, we aimed to establish an in vivo drug-resistant PC model and identify genes involved in GEM resistance. We focused on one of these factors, CITED4, and elucidated its mechanisms of action in GEM resistance in PC.
Methods: L3.6pl, a GEM-sensitive PC cell line, was orthotopically injected into the pancreas of BALB/c nude mice to establish a GEM-resistant PC animal model. Transcriptomic data from control or GEM-resistant tumor-derived cells were analyzed. GEM resistance was evaluated using cell viability, clonogenicity, and apoptosis assays. An apoptosis array was used to identify genes downstream of CITED4. A CITED4 knockout-mediated GEM sensitivity assay was performed in an orthotopic xenograft mouse model using PANC-1 cells, which are GEM-resistant cells.
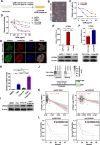
Results: From the RNA sequencing data of isolated GEM-resistant PC cells and The Cancer Genome Atlas dataset, 15 GEM resistance-related genes were found to be upregulated, including CITED4, the gene encoding a type of CBP/p300-interacting transactivator implicated in several cancers. CITED4 knockdown in drug-resistant cells reduced cell proliferation and migration but increased apoptosis. To identify the molecular mechanism underlying CITED4-mediated induction of GEM resistance, alterations in Baculoviral IAP Repeat Containing 2 (BIRC2) levels were observed using an apoptosis array. BIRC2 expression was downregulated following CITED4 knockdown in GEM-resistant PC cell lines. Furthermore, chromatin immunoprecipitation and promoter assays showed that BIRC2 was directly regulated by CITED4. Consistent with the CITED-knockdown experiments, silencing of BIRC2 increased the sensitivity of L3.6pl-GEM-resistant and PANC-1 cell lines to GEM. Furthermore, CITED4 knockout using the CRISPR-Cas9 system in PANC-1 cells increased the sensitivity to GEM in orthotopic mice. Moreover, elevated CITED4 and BIRC2 expression levels were associated with poorer outcomes in human PC clinical samples.
Conclusions: Collectively, these results indicate that CITED4 regulates GEM resistance via inhibition of apoptosis by upregulating BIRC2 expression in PC cells. Therefore, CITED4 may serve as a valuable diagnostic marker and therapeutic target for GEM-resistant PC.
Keywords: BIRC2; CITED4; Drug resistance; Gemcitabine; Pancreatic cancer.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: This study was approved by the Public Institutional Review Board of the Ministry of Health and Welfare (P01-202105-31-011). The animal protocol was approved by the Committee on Animal Experimentation of the Korea Research Institute of Bioscience and Biotechnology. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare that they have no competing financial interests.
Figures





References
-
- Twohig PA, Butt MU, Gardner TB, Chahal P, Sandhu DS. Racial and gender disparities among obese patients with pancreatic cancer: a trend analysis in the United States. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2023;57(4):410–6. - PubMed
-
- Kolbeinsson HM, Chandana S, Wright GP, Chung M. Pancreatic cancer: a review of current treatment and novel therapies. J Invest Surg. 2023;36(1):2129884–95. - PubMed
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2020. CA Cancer J Clin. 2020;70(1):7–30. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

